Posterolateral Rotatory Instability
Definition
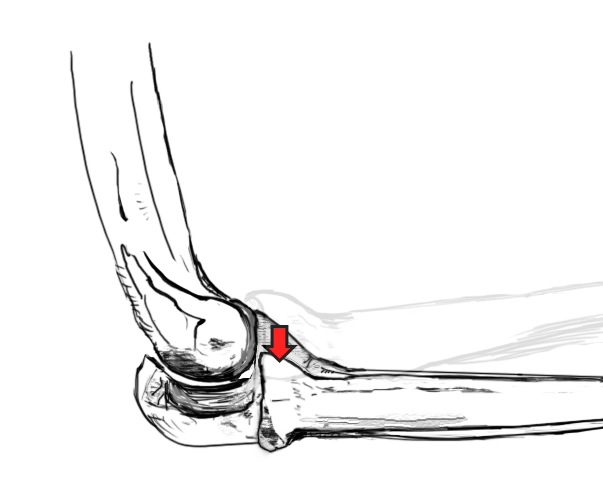
Radius rotates externally in relation to the ulna
- posterior displacement of the radial head relative to the capitellum
- in flexion
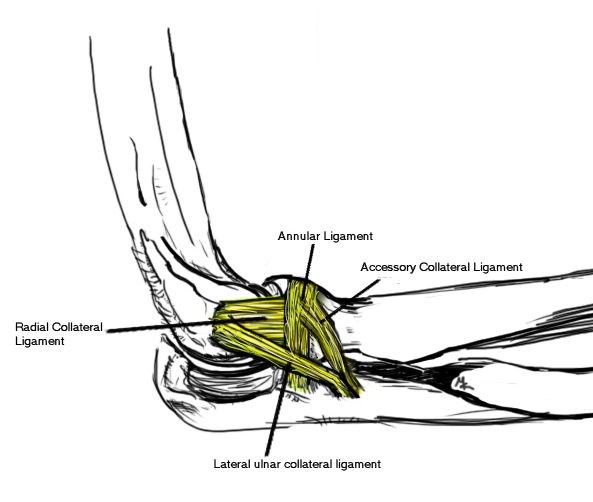
Anatomy LCL
Radius rotates externally in relation to the ulna
- posterior displacement of the radial head relative to the capitellum
- in flexion


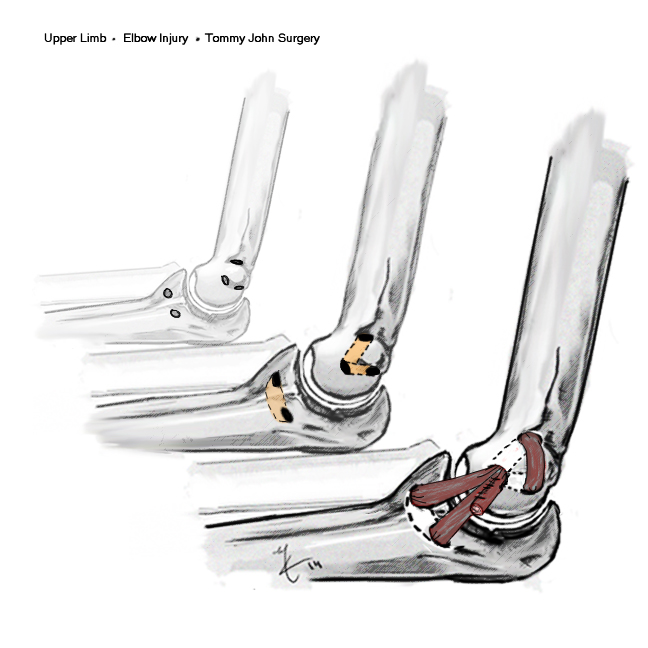
Throwing injury
- seen in the throwing athlete
- repetitive microtrauma / valgus stress
- develop laxity
Initially
- lose velocity / accuracy
Develop medial pain
40% ulna nerve symptoms
1. Removal Loose body
2. Excison of osteophytes
- coronoid
- olecranon
- aiming to improve ROM / prevent impingement
RA
- very good results
- 97% 10 year survival Coonrad-Morrey prosthesis
Other Dx
- OA / post-traumatic arthritis / nonunion
- tend to have worse survival than RA
Haemophilia
- elbow joint commonly involved
- 90% of haemophiliacs
Acute unreconstructable fracture > 60
Very few
- young labourer with severe disabling elbow pain
- trial in POP at 90o for 6 weeks
Poor function
- adjacent joints cannot compensate for loss of function
RA
- high failure rate especially flail elbow with poor bone stock
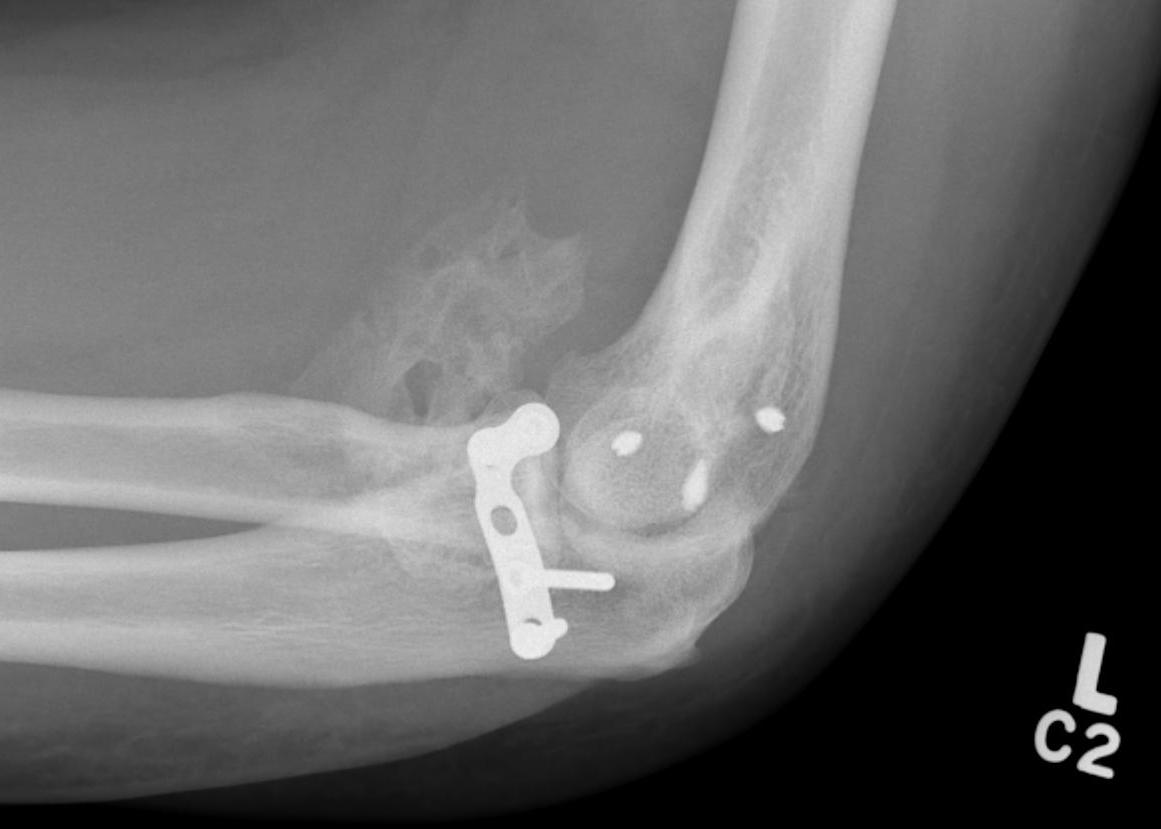
Parosteal OS
- bone is not continuous with cortex in MO
3% incidence in elbow joint trauma to some degree
Relatively rare
Average age 50
Men 4:1 Women
Usually dominant arm
Primary
- associated with strenuous manual labour
Secondary
- trauma
- OCD
- synovial chondromatosis
- valgus extension overload / MCL insufficiency
1. Lower limb
All walk
- Ankle > knee > hip
Ankle
- most require operations for ankles
LLD
- unilateral underdevelopment
- LLD 0-5cm (average 2cm)
2. Lower limb
- one handedness
- decrease movement in swing
- astereogenesis
- usual upper limb contractures