Definition
No good definition
- flexible flat foot
- medial longitudinal arch of foot in weight-bearing is in contact with ground or closer to ground than 'normal'
Epidemiology
Common
- almost always bilateral
- strong familial tendency
Aetiology
Physiological
All infants have flat feet
- at birth foot is in calaneovalgus & there is no medial arch
- when child begins to walk, feet evert & ER
- foot has large medial fat pat
Arch begins to develop in 2nd & 3rd year to variable degree
Thus flatfeet are
- usual in infants
- common in children
- in normal range for adults
Compensatory
Due to another anatomical variation
1. Genu Valgum
- physiological knock-knees most pronounced at age 3-4
- leads to apparent flatfoot
- corrects by ~ age 6
2. Out-Toeing
- ER of foot causes body weight to fall anteromedial to ankle
- result is valgus of heel & flatfoot
3. Tight Tendo achilles
- lack of DF compensated by heel eversion & forefoot pronation
4. Joint laxity
- i.e. Marfan's, Ehlers-Danlos
History
Almost always asymptomatic
- may cause aching midfoot
- pain incidence may equal general population
Examination
On weight bearing have combination of
- flat longitudinal arch
- pronated forefoot
- valgus heel
Flexible flatfoot
1. Foot appears normal when suspended / NWB
2. Recreation of longitudinal arch & heel varus on toe raise / windlass
3. Recreation of longitudinal arch by passive DF of Hallux (Jack's test) with weight bearing
4. Mobile or hypermobile STJ
5. Weight bearing callus on lateral longitudinal arch
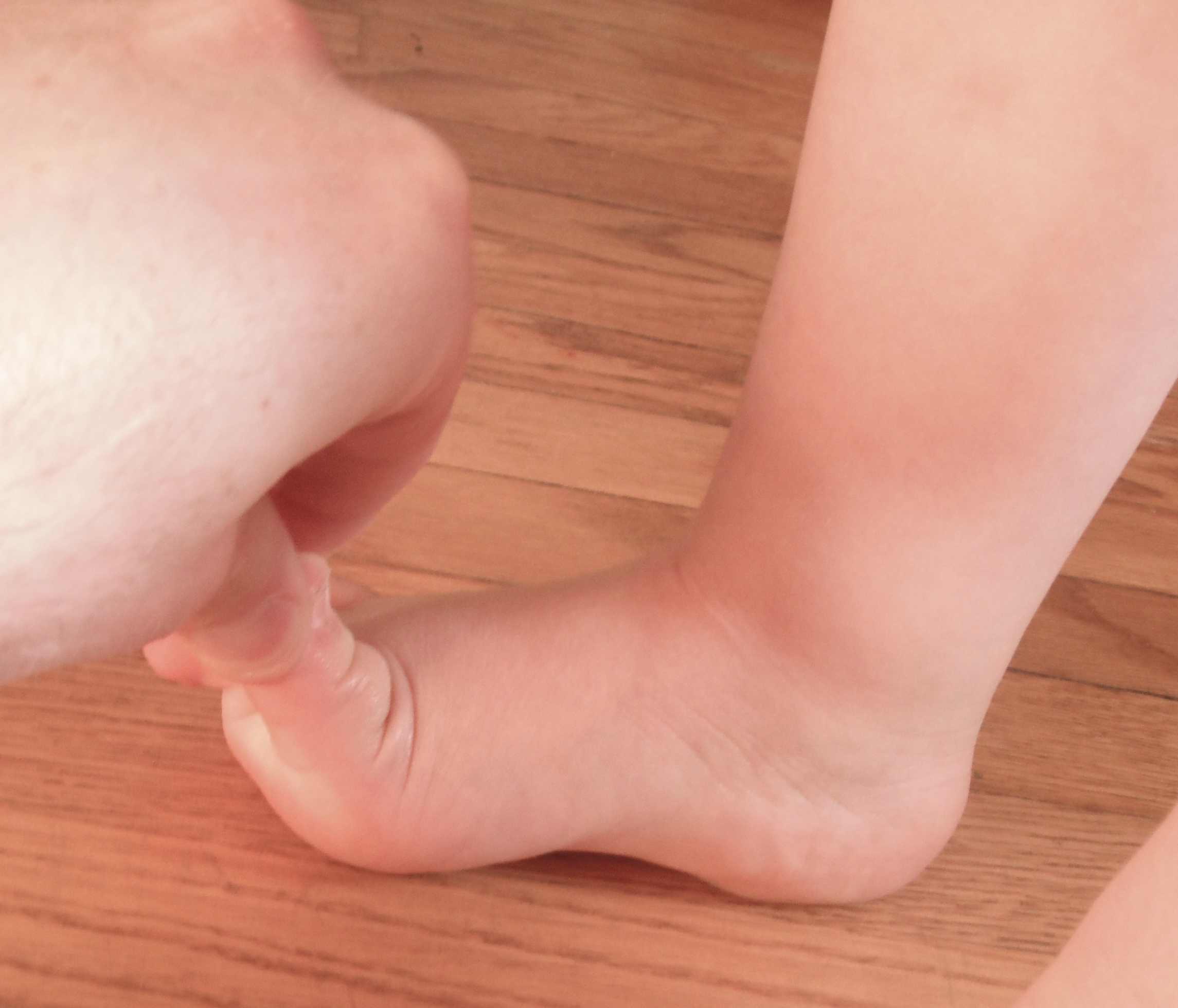
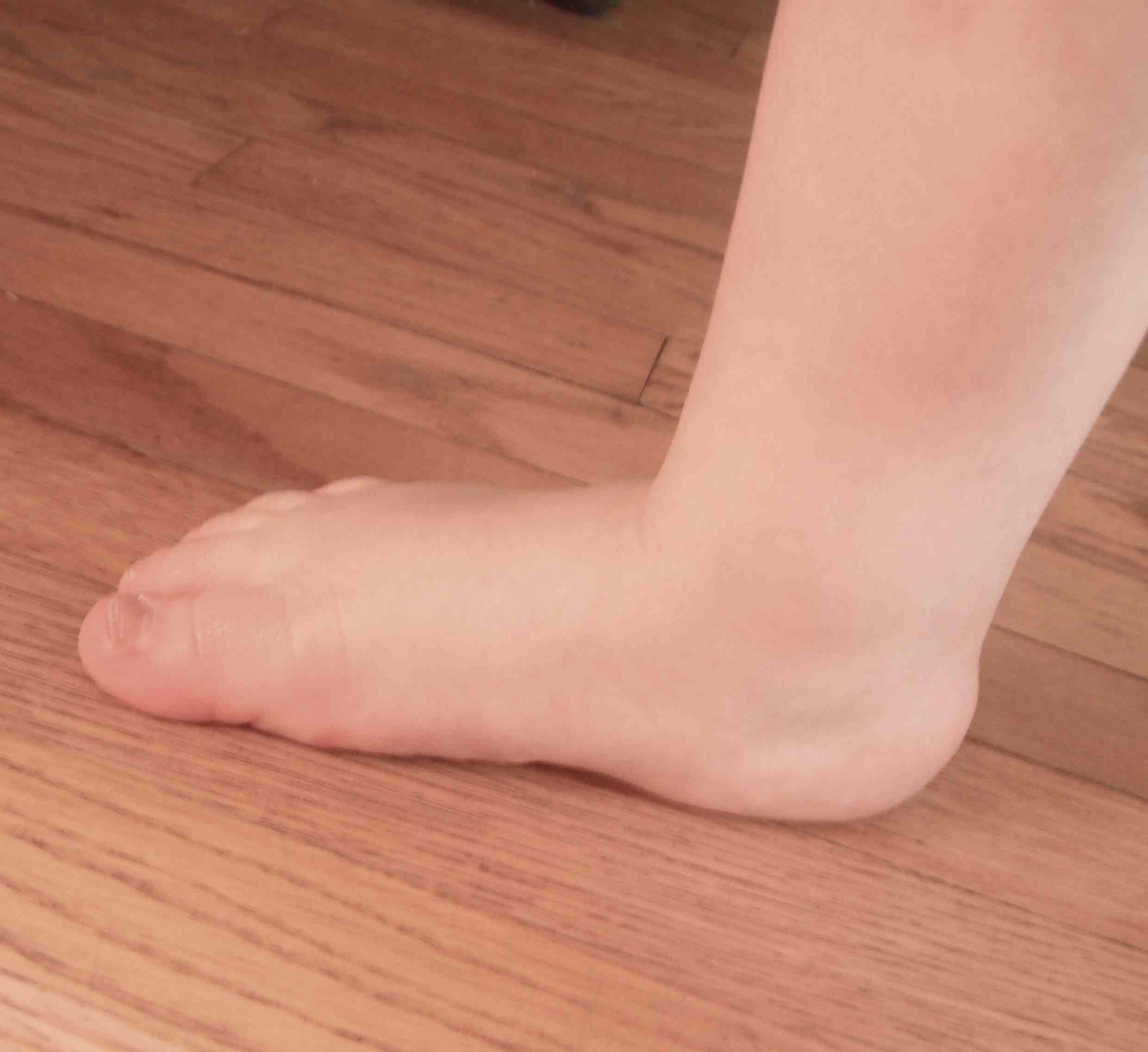

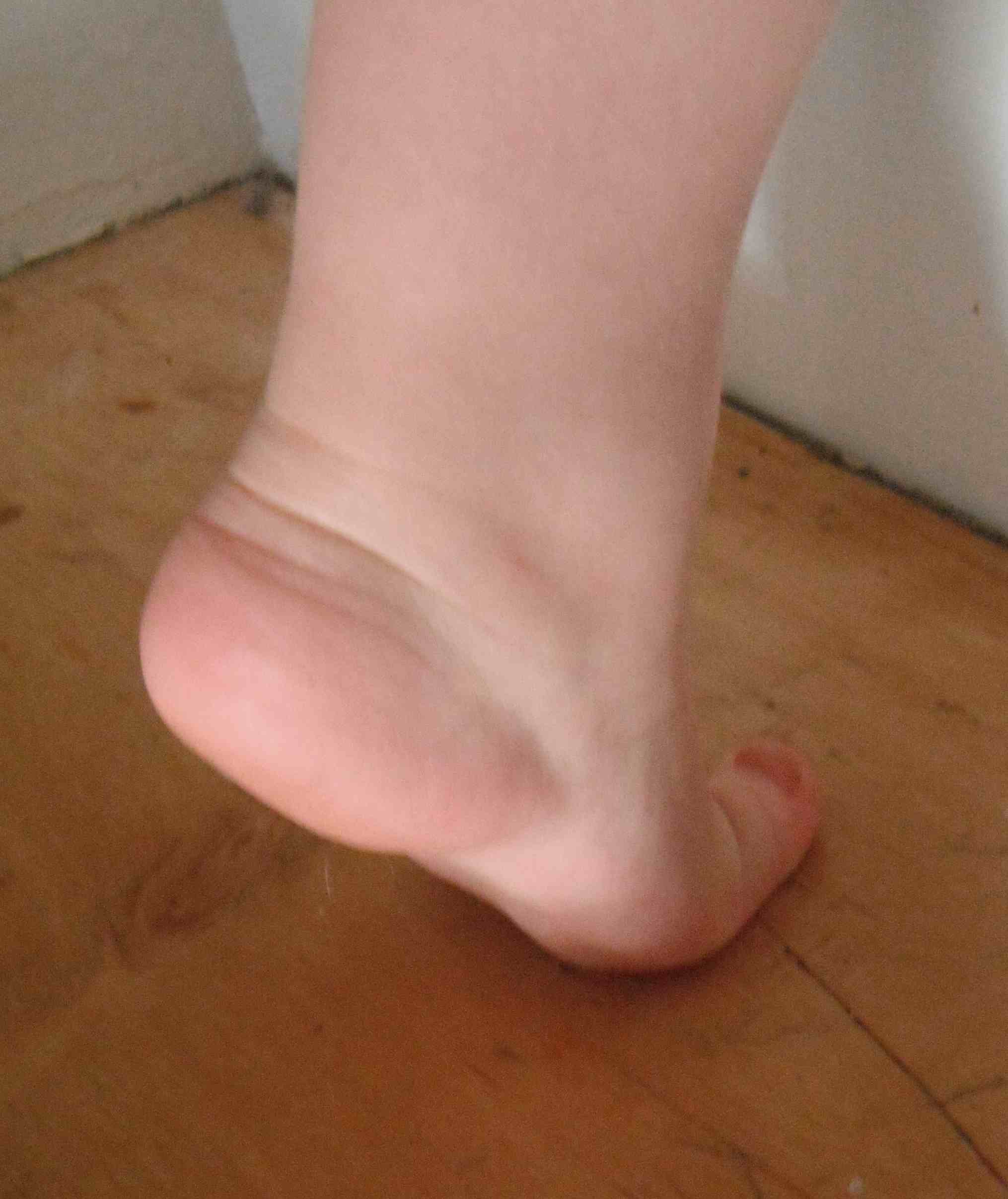
Must look at back
- exclude spinal dysraphism
DDx
Congenital
Flexible
- compensatory - tight T achilles / out-toeing / genu valgum
- physiological
Rigid - CVT / tarsal coalition / skewfoot
Acquired
Trauma - midfoot fracture / Lisfranc / rupture spring ligament / rupture plantar fascia
Neuromuscular - CP, spina bifida, polio
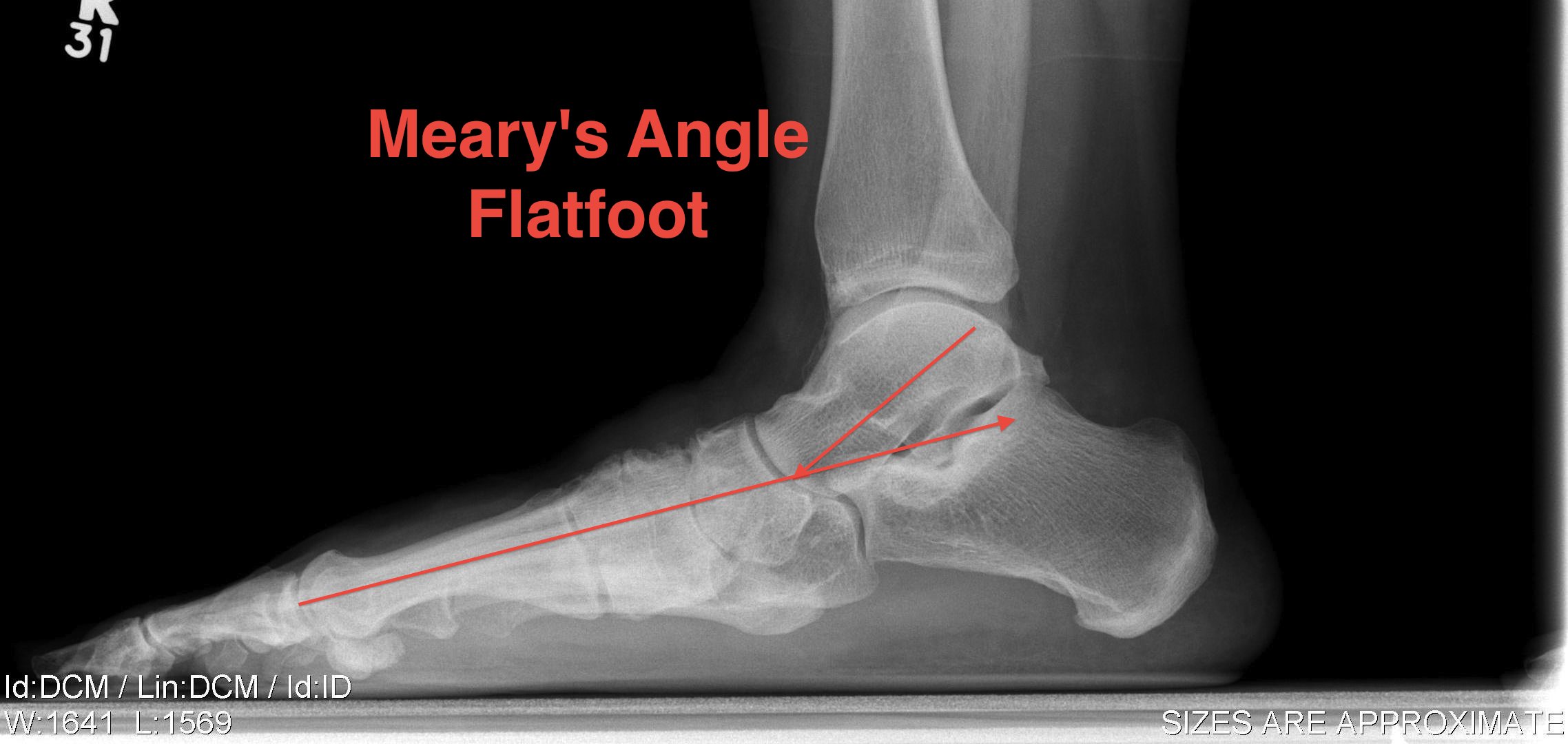
X-rays
Weight bearing lateral and AP
- Meary's angle - talo - first metatarsal < 100
Harris axial / oblique for coalition
Cobey's
- hindfoot alignment view
- see that calcaneum is under the fibula not tibia
CT
Look for coalition
MRI
Identify
- coalition
- inflammatory arthritis
- tibialis posterior dysfunction
Management
Non-operative
NHx
Usually resolves by age 5 or 6
- 20% adults have some degree of asymptomatic flexible flatfoot
- no treatment needed unless symptomatic
Some patients will suffer from midfoot pain
Orthoses
Results
Wenger 1989 JBJS
- orthoses & shoe modifications have no effect on outcome
Will not reverse pes planus
Indications insoles
- relieve pain
- allay parental anxiety
- improve life of footwear
Options
- soft - heel cup + arch support
- hard - custom moulded insole / UCBL insert
Operative
Indication
Disabling pain not responsive to non-operative measures
Options
Skeletally immature
- Grice arthrodesis
- subtalar arthroesis + plantarflexing medial cuneiform osteotomy
Skeletally mature
- medial sliding calcaneal osteotomy
- lateral column lengthening + 1st metatarsal plantarflexing osteotomy
Subtalar arthroeresis with plantar flexing medial cuneiform osteotomy
Concept
Sinus tarsi implants
- axis altering device / blocking
- resist excessive pronation
- prevent adaptive changes
Lateral column lengthening / Evans procedure + 1st Metatarsal Osteotomy
Concept
Lengthen lateral column
Have to combine plantarflexion first MT osteotomy to enable toe to touch floor
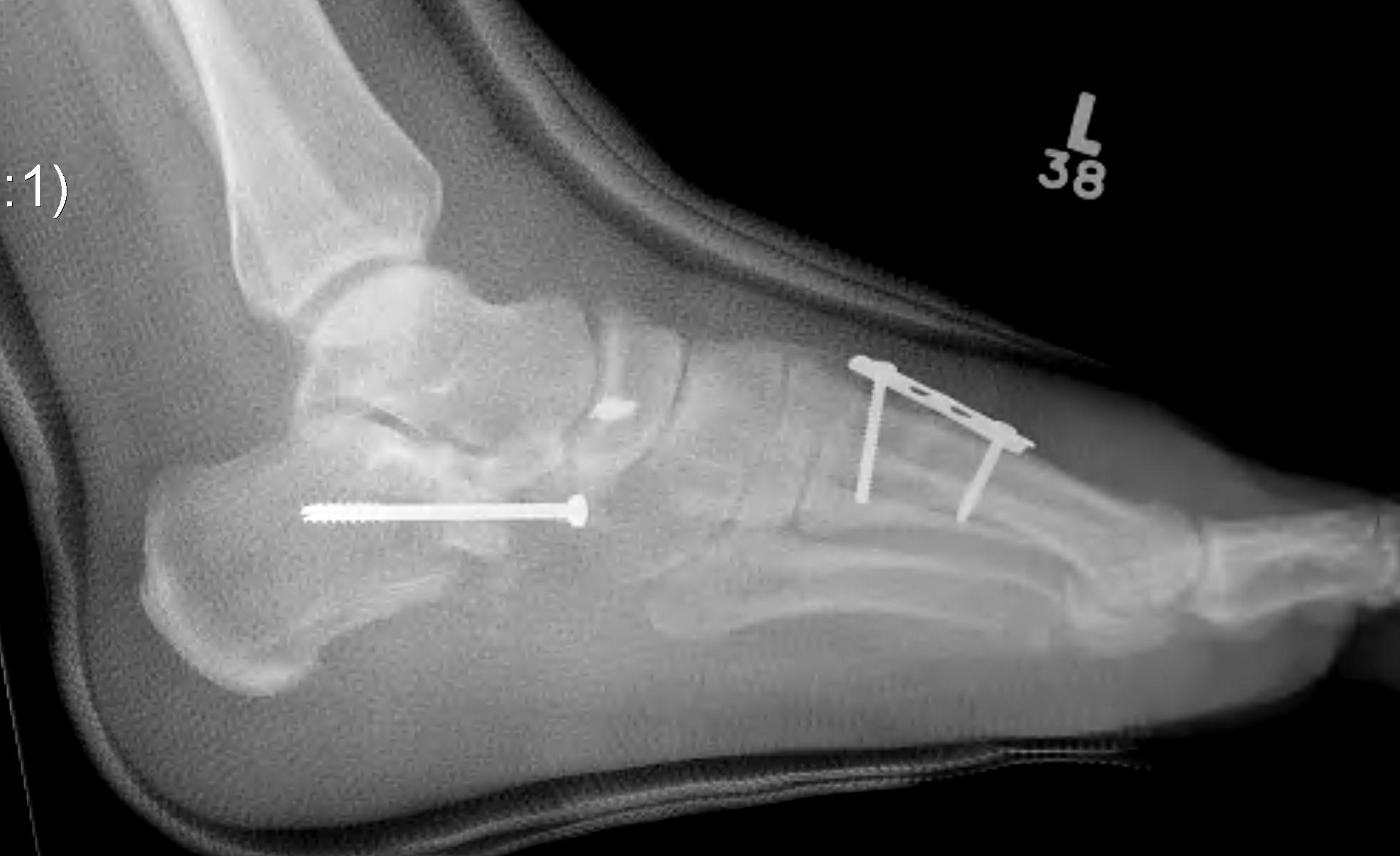
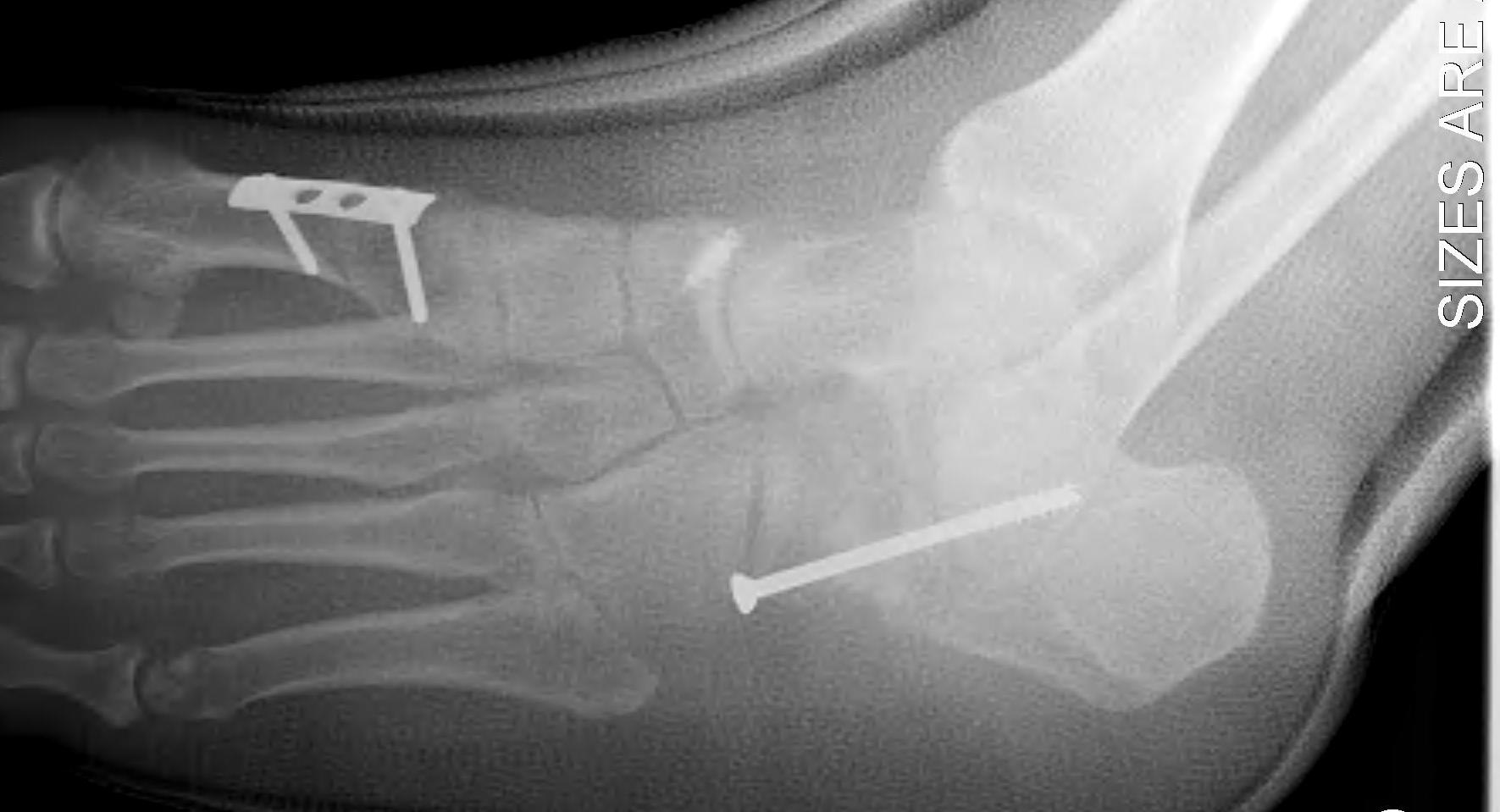
Technique
Incision
- oblique Ollier's / from tip of fibula
- must preserve peroneals and sural nerve
- reflect peroneals superiorly
- elevate EDB
Osteotomy
- 1.5cm proximal to CCJ
- vertical incision in periosteum
- osteotomy between middle and anterior facets medially
- care to protect medial NV bundle
Lengthening
- use osteotome to free medially
- lamina spreader
- open 1 cm, bone graft
- fixation varies - plate, staple
Medial incision
- medial reefing of spring ligament
- tightening of tibialis posterior +/- FDL transfer
First metatarsal plantarflexion osteotomy