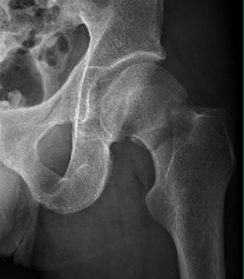
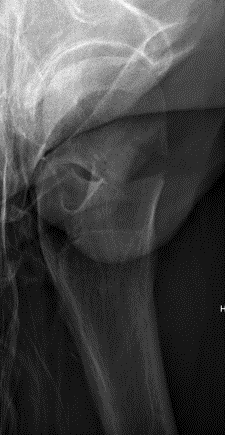
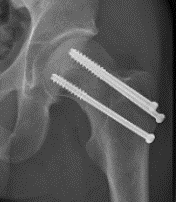
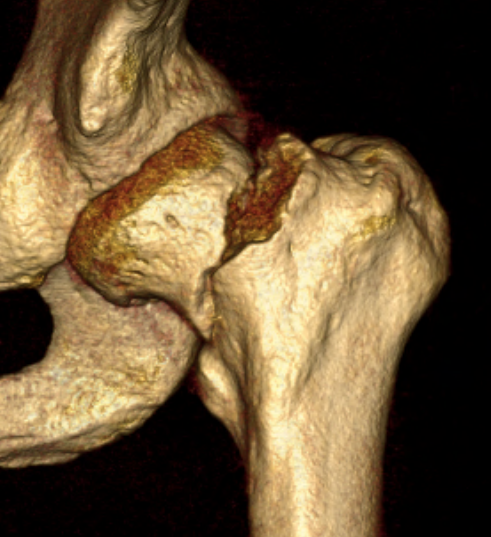
Indications
Displaced fracture - risk of AVN and nonunion
Patient too young for THA
Issues
Vumedi approach to young displaced femoral neck fracture
Timing of surgery
Closed versus open reduction
Capsulotomy
Open approach - Smith-Petersen versus Watson Jones
Fixation - screws / DHS / FNS +/- medial buttress plate
Timing of surgery
Papakostidis et al Injury 2015
- systematic review of 7 studies
- no association between timing of surgery and AVN
- increased incidence of nonunion with surgery > 24 hours
- retrospective review of displaced fractures in 29 patients < 60
- significant reduction in AVN if fixed within 12 hours
Closed versus open reduction
Union rates increased with anatomical reduction
- RCT of 92 patients with displaced subcapital fractures < 50 years
- randomized to open versus closed reduction
- no difference in union rates between groups
- increased nonunion with non anatomical reduction
Haidukewych et al JBJS Am 2004
- 51 displaced subcapital fractures < 50
- 10% incidence of nonunion
- 27% osteonecrosis
- nonunion 4% with good to excellent reduction
- nonunion 80% with poor reduction (>10 mm of displacement, >20°, any varus)
Assessment of reduction
1. Femoral neck shaft angle
2. Restoration of Shenton's line
Closed reduction / Leadbetter Maneuver
FATI CAR
- Flexion / Adduction / Traction / IR
- Circumduction / Abduction
- Reduction check in extension
- "Foot in Palm Test"
- if sufficiently reduced will sit without ER
Capsulotomy
Theory
- there is evidence of increased hip intracapsular pressure after fracture
- this may reduce blood flow to the femoral head
No conclusive evidence that capsulotomy reduces rates of AVN
Options with closed reduction
- percutaneous needle / knife drainage of hematoma
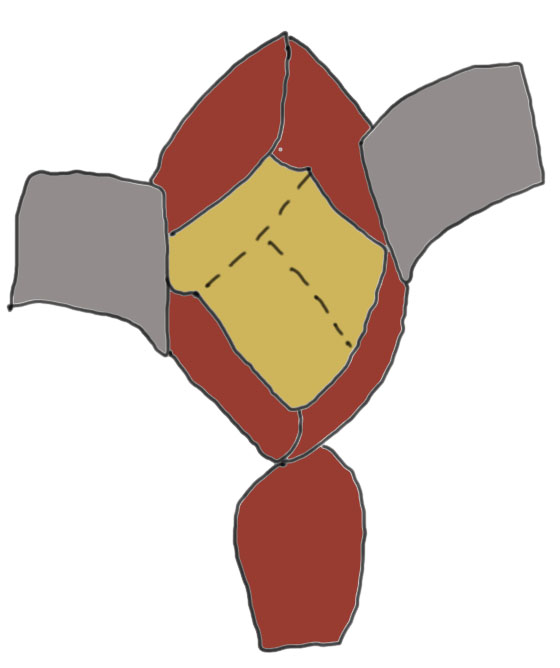
Approaches
Smith Petersen
- direct visualization of fracture
- likely better to allow anatomical reduction
- easier to do medial plating to hold reduction prior to definitive fixation
- need separate approach for fixation
Watson Jones
- less direct visualization of fracture
- same approach for fixation
Technique Smith Petersen Approach
Vumedi technique Smith Petersen
Radiolucent table + floppy lateral with sandbag under affected hip
Vertical incision below ASIS
Superficial dissection
- between TFL (lateral) and sartorius (medial)
- interval more clear distally
- divide fasica over TFL with LFCN medial
- reflect muscle of TFL laterally
Deep dissection
- between G medius laterally and direct head rectus femoris medially
- +/- tenotomy of direct head rectus femoris
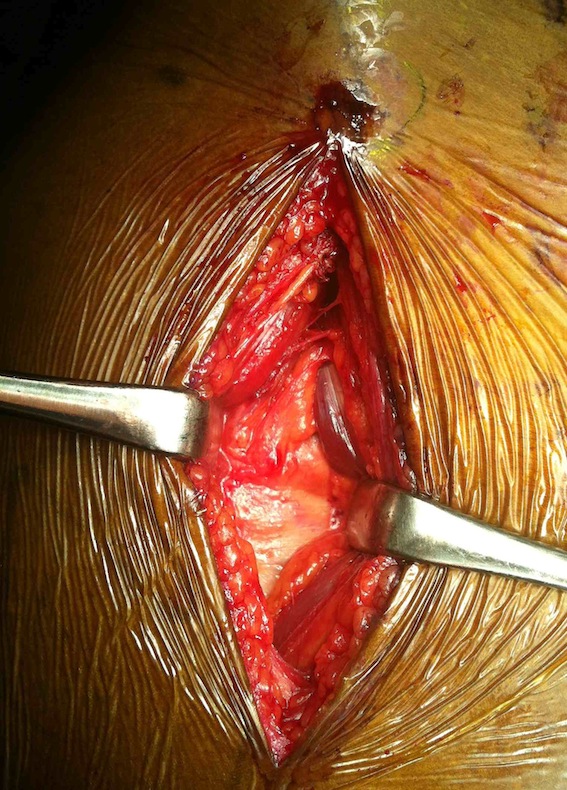
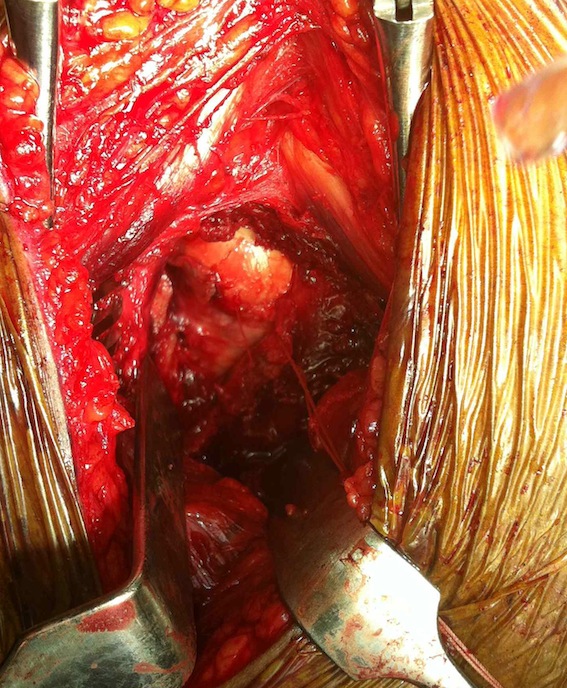
Smith Petersen anterior approach, with capsulotomy and reduction with pins
Technique Watson Jones approach
Radiolucent table + floppy lateral with sandbag under affected hip
Lateral incision between anterior aspect greater trochanter and ASIS
Flexing hip 20-30o helps exposure
Superficial dissection
- identify interval between gluteus medius and tensor fascia lata (TFL)
- divide fascia lata
- identify fat pad inferiorly, muscle gluteus medius superiorly
- develop this interval to anterior femoral neck
- lateral femoral circumflex artery in this interval
- place retractors over inferior femoral neck and superior femoral neck
Deep dissection
- remove fat pad
- release reflected head of rectus femoris off anterior capsule
Capsulotomy
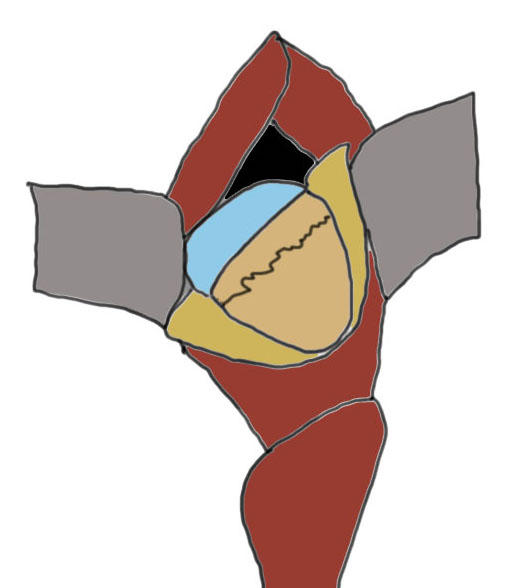
Capsulotomy
- transverse limb at head neck junction to preserve blood supply
- vertical down centre of femoral head
- avoid dissecting superior aspect of femoral neck where major artery of MCFA runs
- tag and reflect capsule
- place retractors inside the capsulotomy to expose the femoral neck
- can place superior retractor on ilium
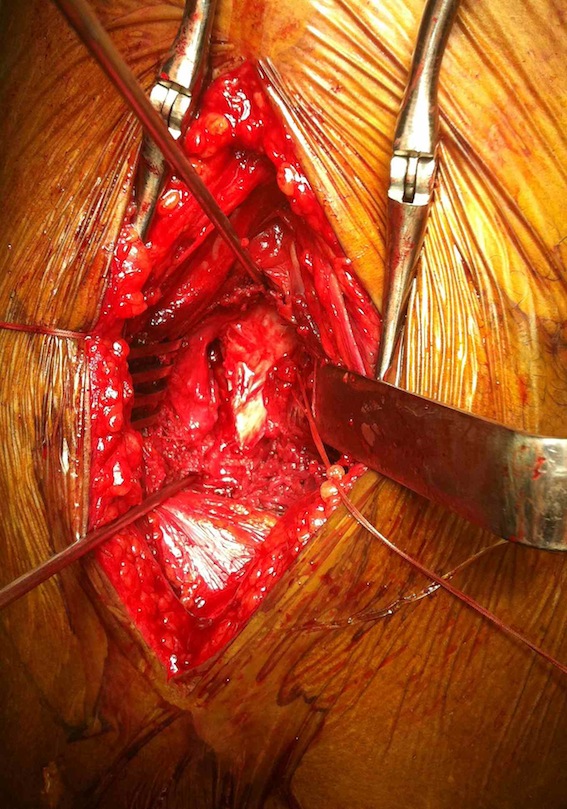
Reduction techniques
Obtain anatomical reduction under direct vision
- Steinman pin in femoral head
- second Steinman pin in femur to correct external rotation force
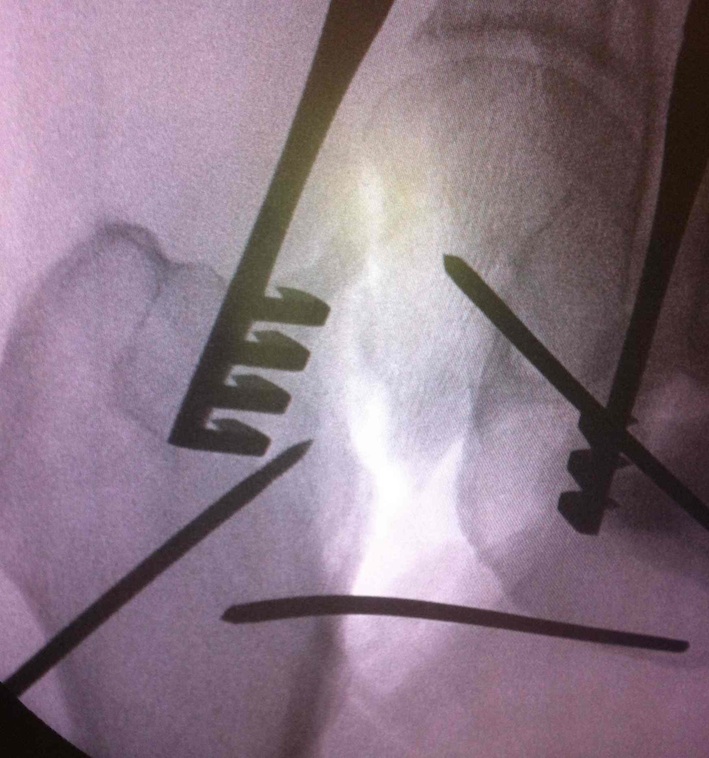
Check reduction on image intensifier
- ensure no varus on AP
- obtain lateral by adducting and IR hip / ensure good reduction on lateral

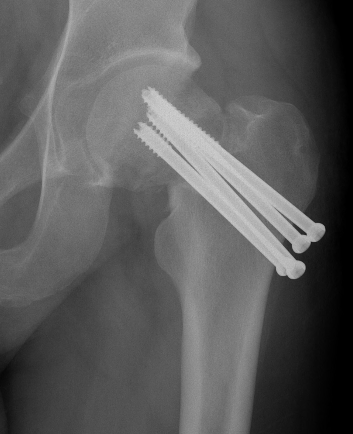
Fixation
DHS /Cannulated screws / FNS
Unstable fracture - augment with a medial buttress plate on inferior neck
Medial buttress plate
Non-Union
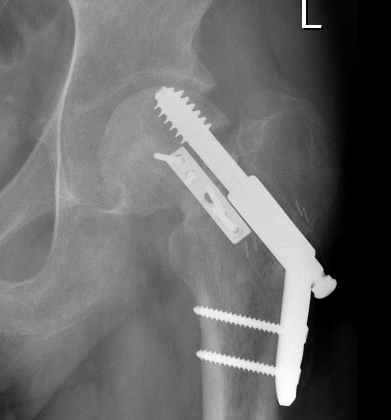
Options
Valgus osteotomy
THA
Valgus osteotomy
Aim
- convert shear forces into compressive forces across fracture
Indications
- patient must have at least 15o adduction
Template
- aim to reduce the angle of the neck fracture to between 20 - 30o from horizontal
- measure angle of fracture from horizontal (usually 40 - 50o up to 70o)
- difference is angle of correction (20 - 30o)
Technique
Vumedi valgus osteotomy femoral neck fracture nonunion
Results
Norouzi et al Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2009
- 33 cases of nonunion of femoral neck fracture
- combination failure post surgery and missed / neglected fractures
- union in 32/33 after 5 months with valgus osteotomy
