Indications
TFCC tears
SL instability
Dorsal wrist ganglion
Scaphoid fracture with percutaneous pinning
Distal radius fracture
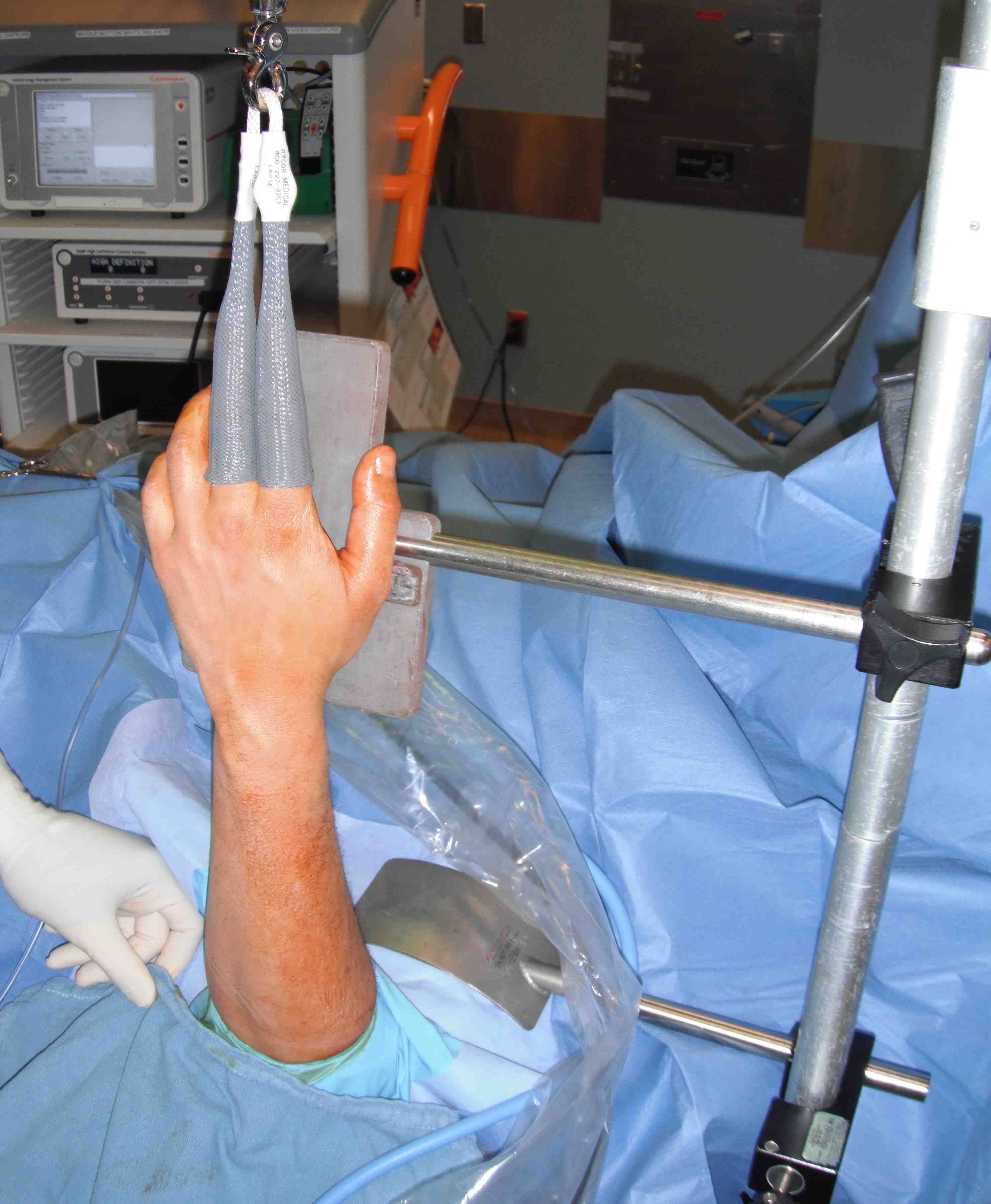
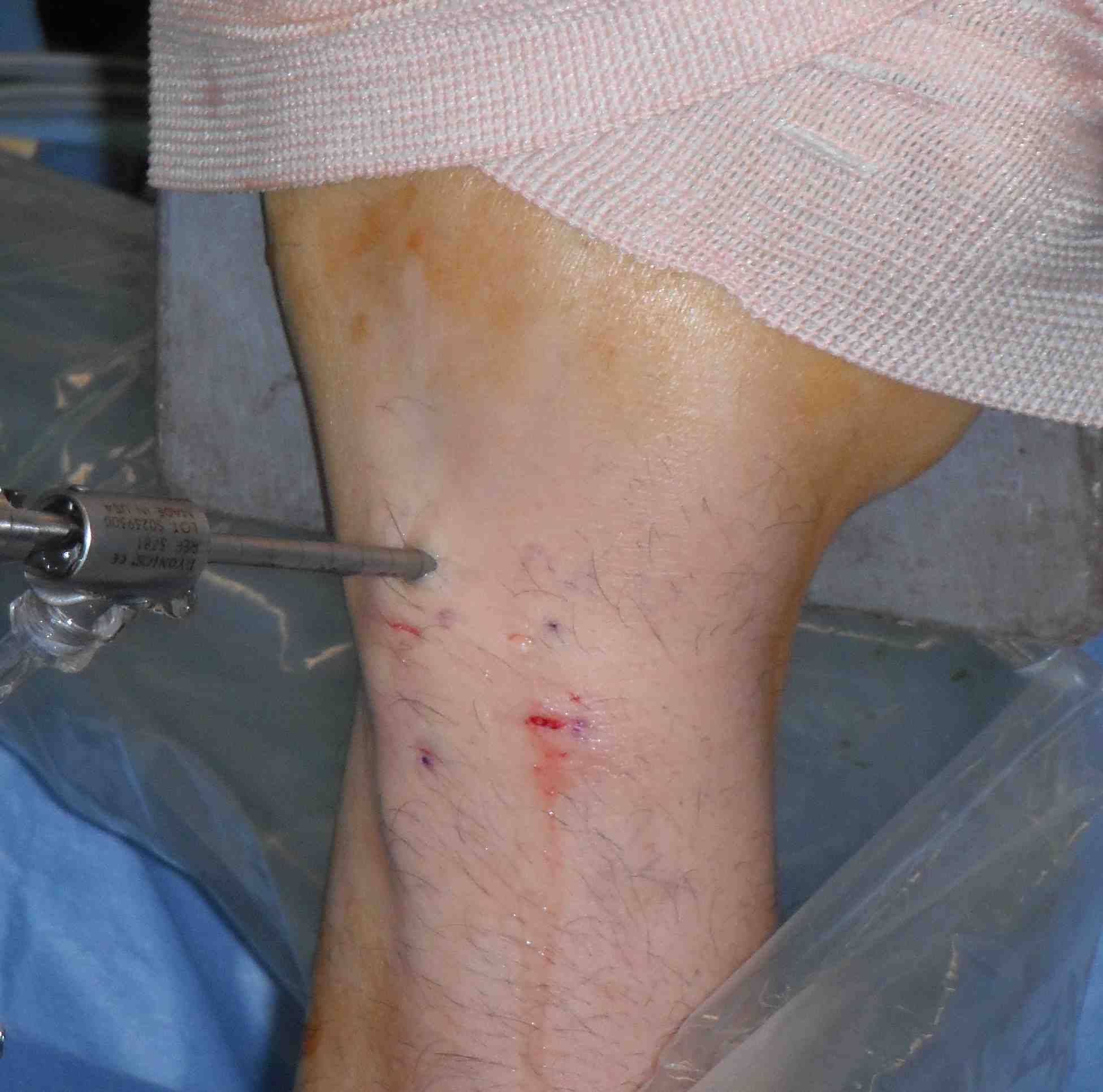
Setup
Tourniquet
Finger Traps Index & middle
Overhead traction device
2.7 mm scope / small joint instrumentation
- insufflate with saline first at 3-4
Radiocarpal Joint
RCJ is U shaped
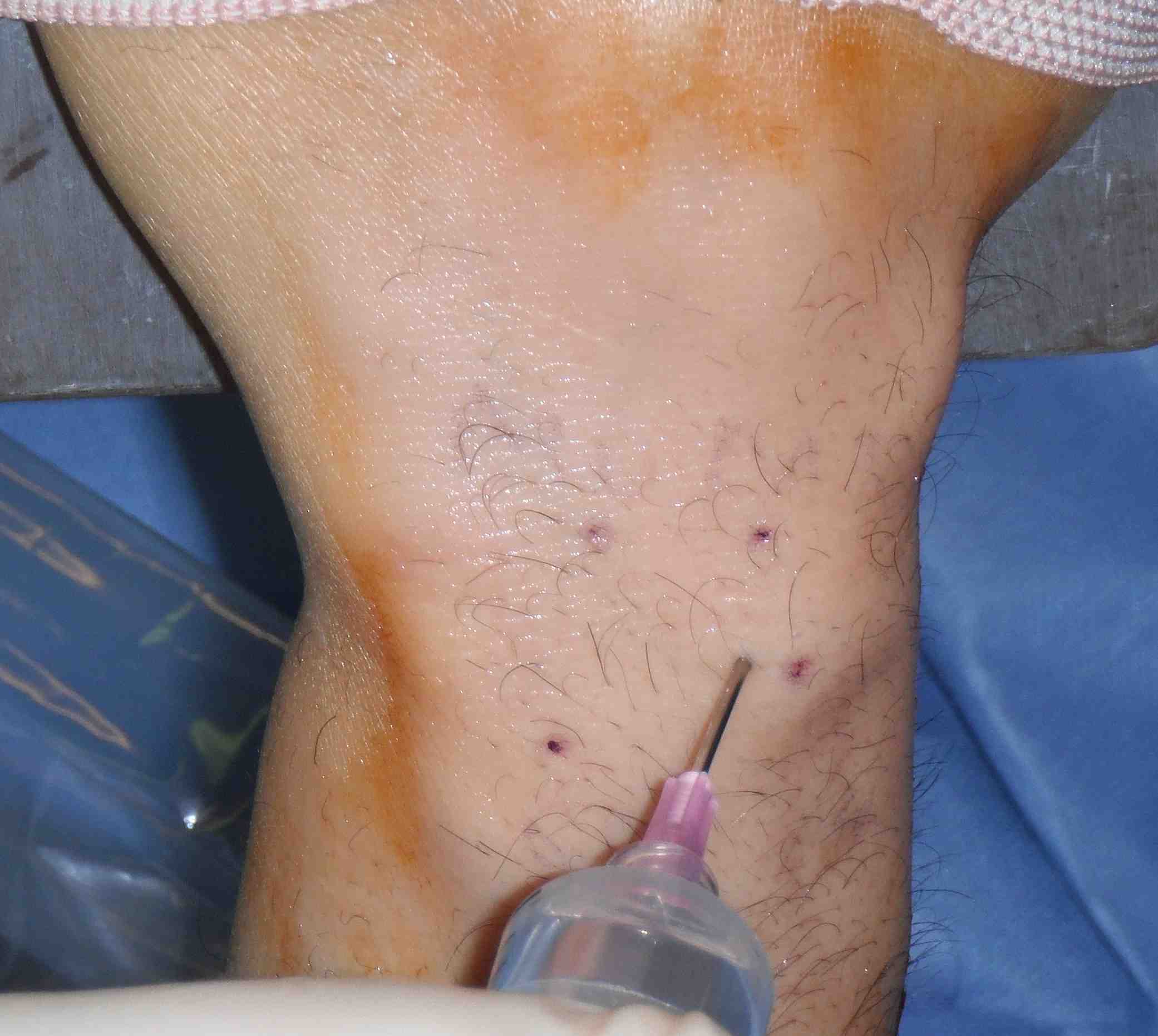
Portals are between extensor compartments
- longitudinal incisions to protect extensor tendons
- blunt dissection to preserve SRN branches
- angle 30o volar due to shape distal radius
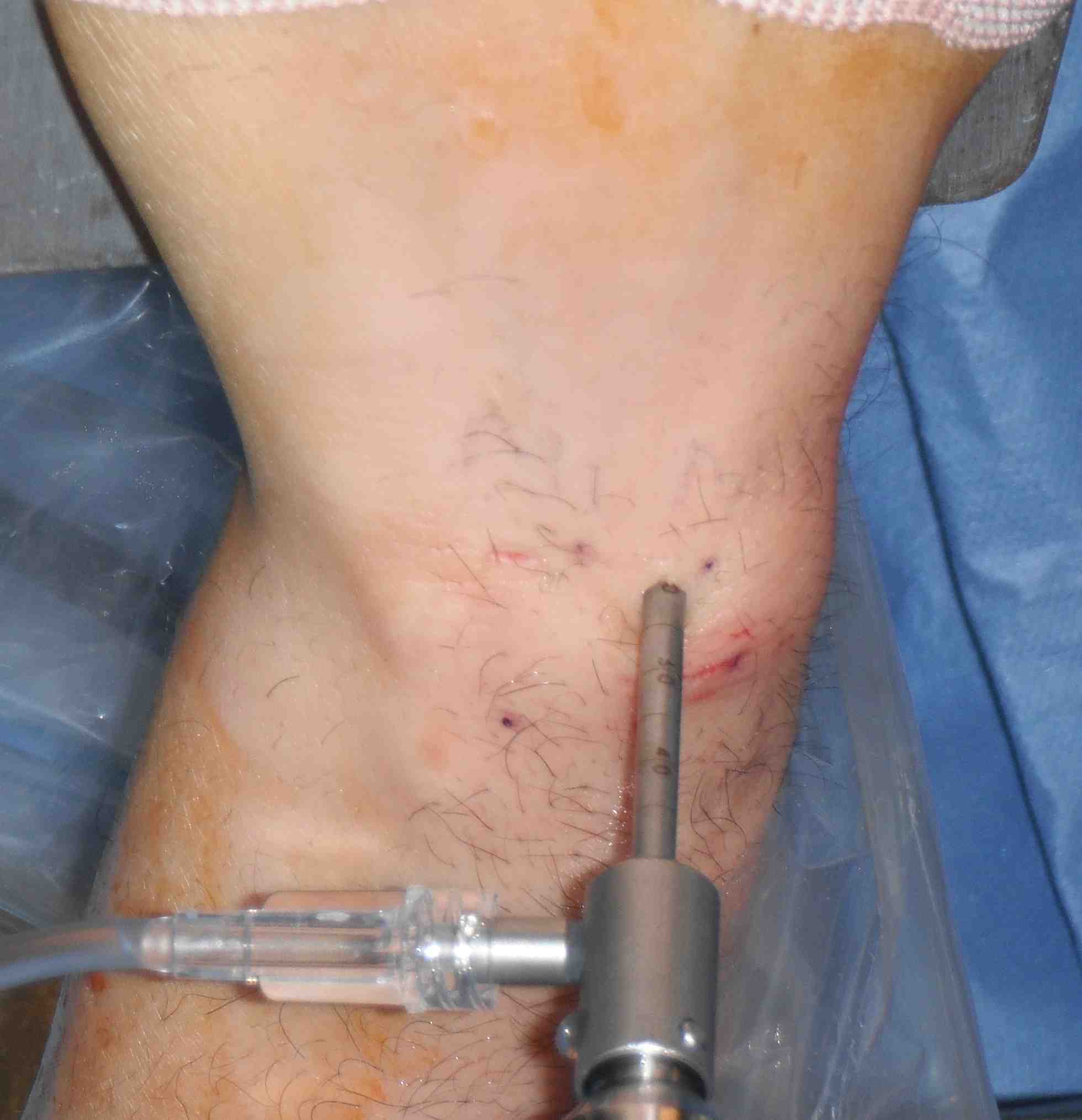
3-4 Portal
- feel Lister's tubercle
- 1 cm distal is soft spot between 3 and 4
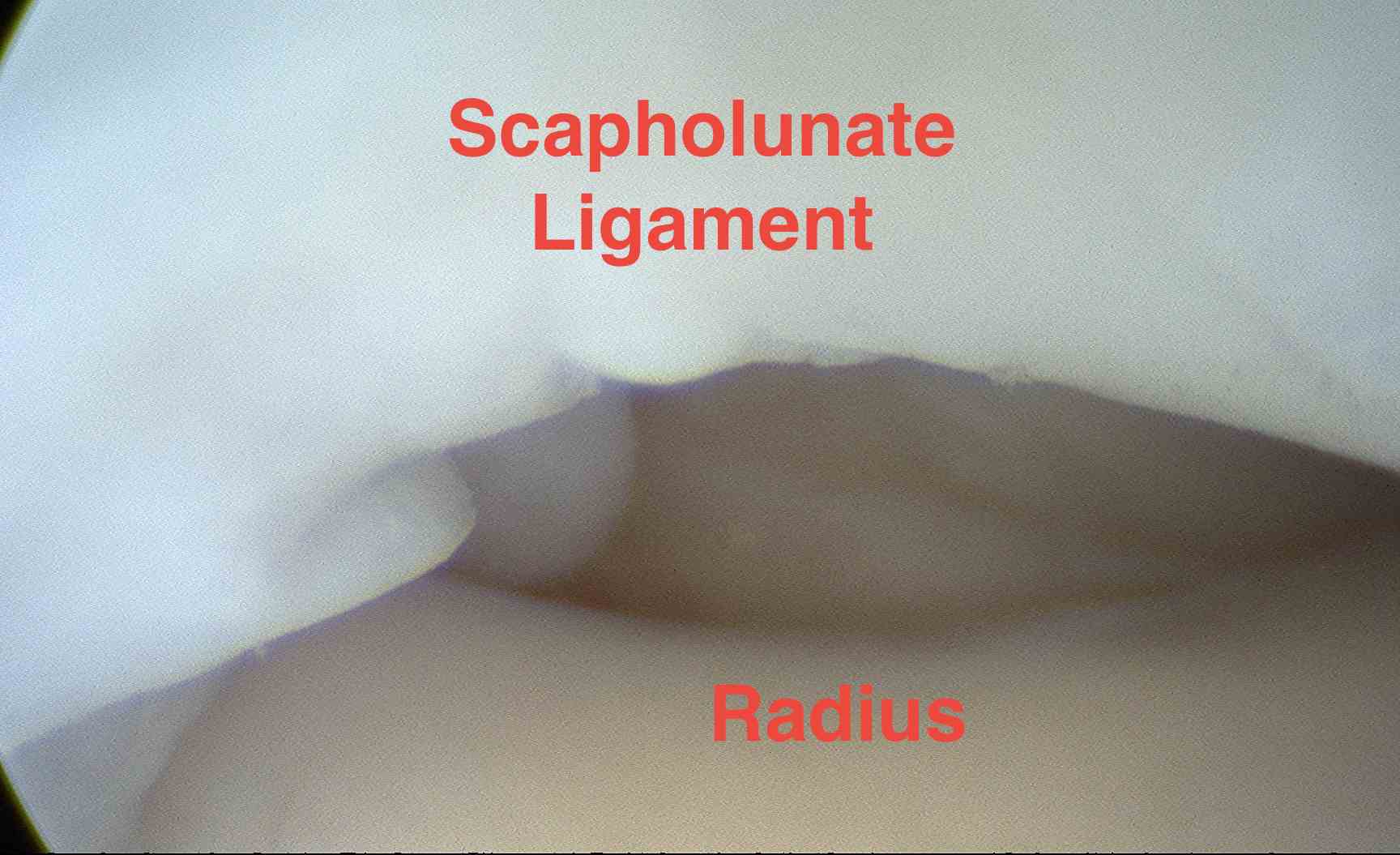
- between distal radius and scapholunate
- primary viewing portal
4-5 Portal
- roll finger over mobile 4th compartment
- feel soft spot
- slightly proximal to 3-4 because of slope of radius
- between distal radius and lunatetriquetral
- instrumentation
6-R and 6-U
- Named after their position about ECU
- 6-R working
- 6-U inflow
Midcarpal Joint
Anatomy
MCJ is S shaped
- midcarpal & radiocarpal have separate synovial cavities unless the SLL is torn
Midcarpal radial / MCR Portal
- 1 cm distal to 3/4 portal
- radial side of the third metacarpal axis
- in line with Lister's tubercle
- soft depression between the capitate and scaphoid
- working portal
Midcarpal ulna / MCU Portal
- 1 cm distal to 4/5 portal
- in line with 4th metacarpal
- distal to lunate-triquetral joint
- proximal to capitate and hamate

Radiocarpal Joint
Start at radial styloid and scaphoid
- work radial to ulnar
Distal radius
RSC Ligament
- immediately beside is Long RLL
- is extremely wide usually x3 RSCL
- next is short RLL
- often see blood vessels along this ligament
Scapholunate ligament
- examine from membranous prox portion to thicker dorsal ligamentous portion
TFCC
Follow ulnarly along lunate and its fossa
- should be taut like a trampoline
- actual ballottement with probe should give same feeling
- trampoline test
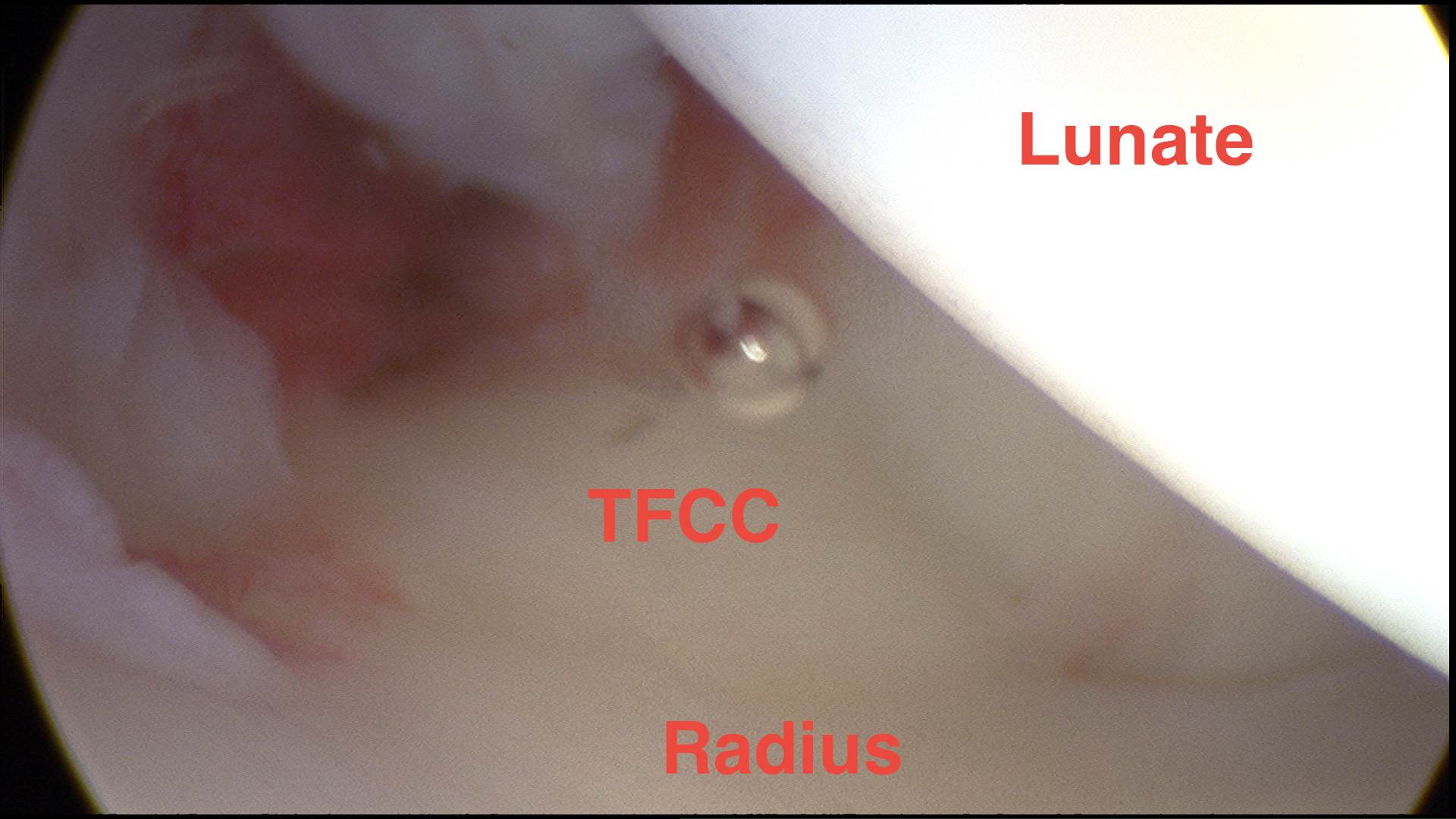
Examine for tears
- central or peripheral
- ulnar styloid recess is normal finding at base of styloid not a tear
Lunate chondromalacia
Midcarpal joint
Curved of head of capitate
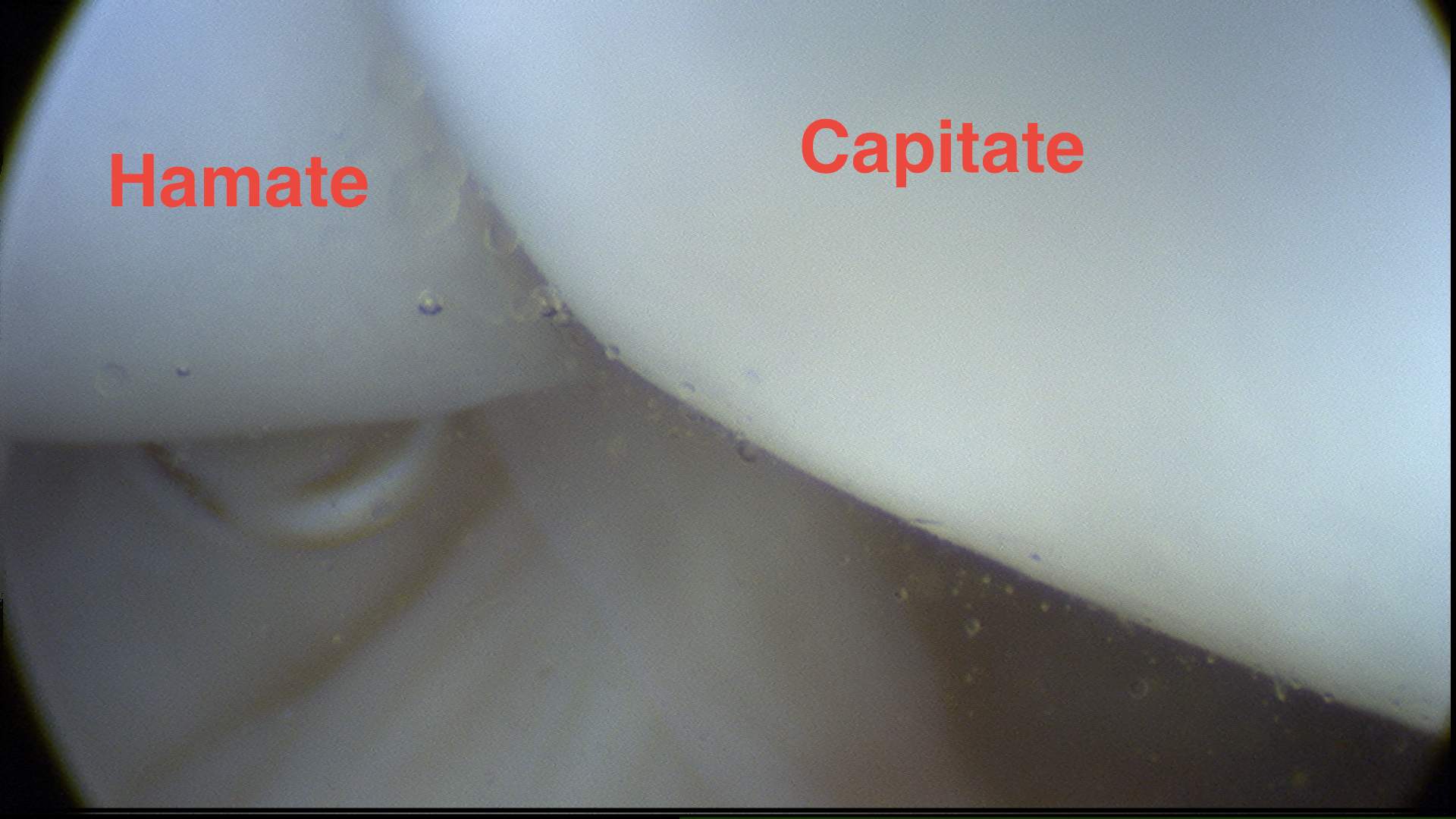
SL joint
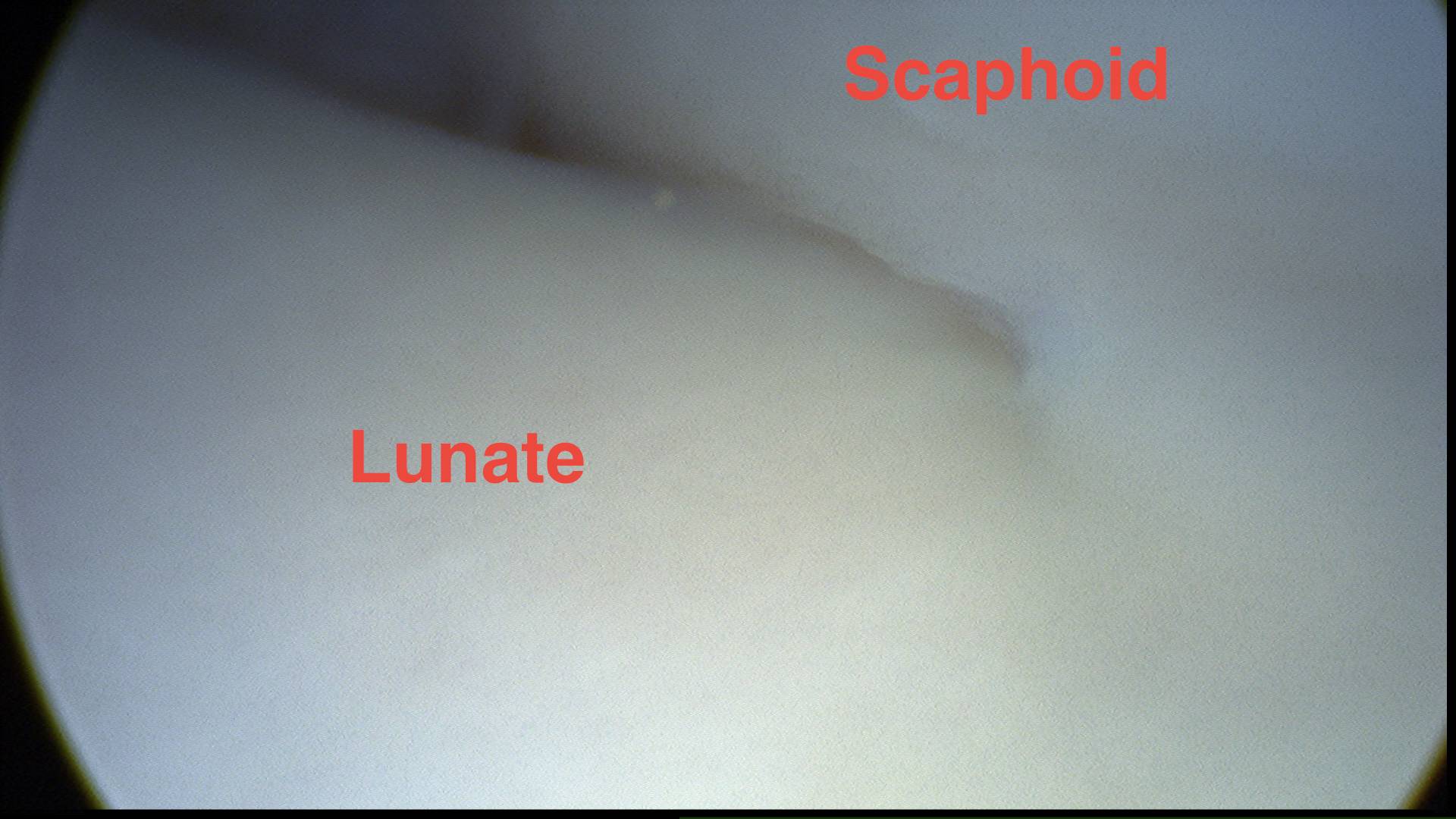
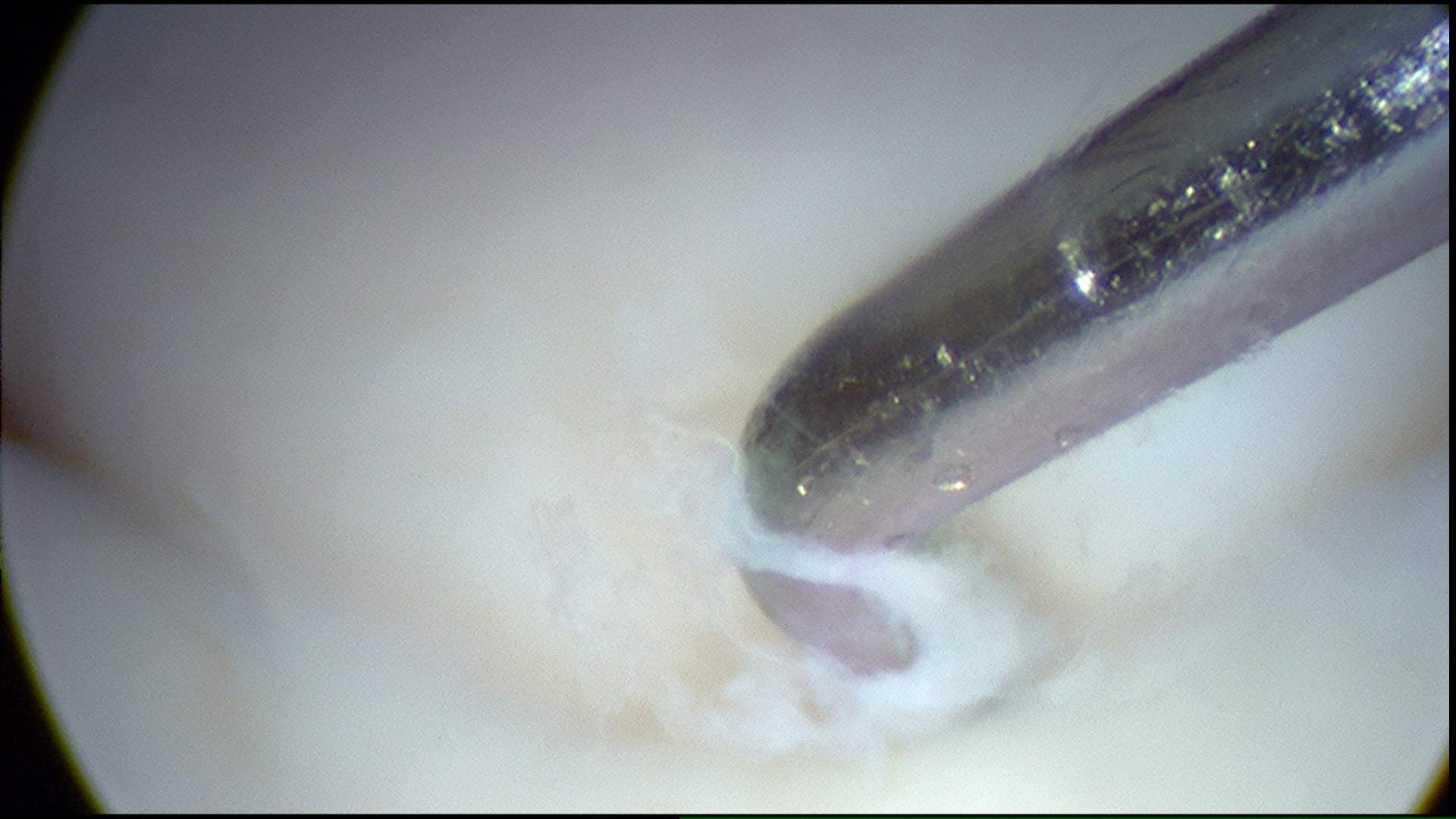
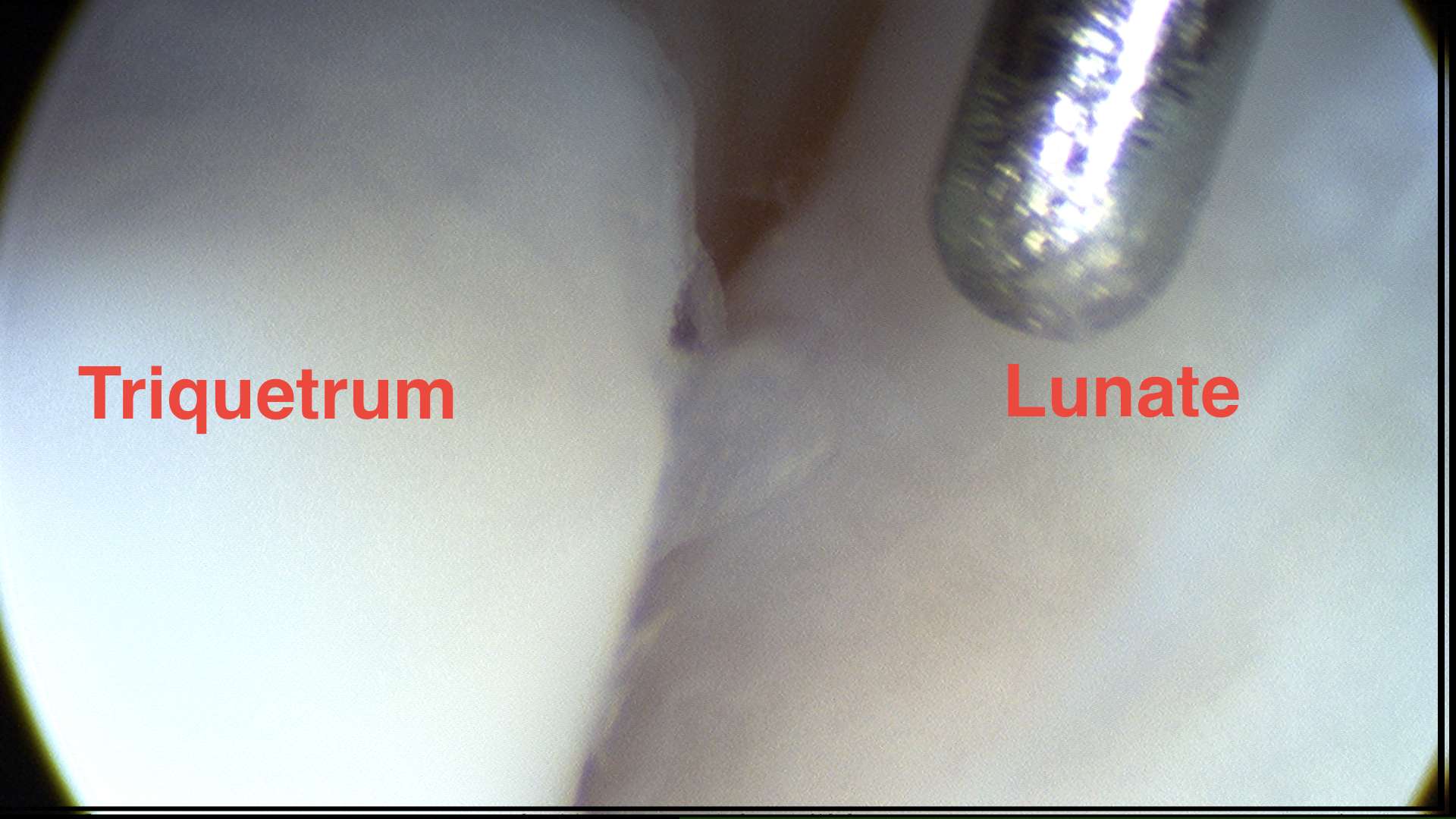
Lunate-triquetral joint
Specific Conditions
Carpal Instability
SL and LT Ligaments
- must look from radiocarpal and midcarpal joints
- both joint ligaments should be tight and concave
- if inflow in RCJ with midcarpal outflow have tear in ligament
Arthroscopic classification
1. Attenuation or haemorrhage within ligament
- no step
- can debride partial tears with good results
- Rx cast immobilisation
II. Incongruency or step-off in midcarpal space
- Use k-wire as joy stick to reduce
- treat with arthroscopic pinning
- 80% reported good results
III. Step-off on both sides
- pprobe may be passed between bones
- treat with arthroscopic or open repair
IV. Gross instability
- open repair
TFCC Injuries
Use 4-5 portal as visual portal and 6-R as working portal
Issues
- degenerative or traumatic
- central or peripheral
- with or without DRUJ instability
- without or without chondromalacia
- radial or ulnar avulsions
- +/- Styloid fracture
Techniques
Debride central tears acute or degenerative
Attempt repair of peripheral tears
Unstable DRUJ
- reinforce DRUL or PRUL with strip of ECU
Degenerative tear and ulnar plus
- add ulnar shortening to debridement
- can perform arthroscopic wafer procedure
