Definition
Replant
Reattachment of body part that has been completely severed
Revascularisation of incomplete amputation
Vascular repair is necessary to prevent necrosis of the extremity
- retains some venous and lymphatic drainage albeit small
- revascularisation easier, quicker and better results
Mechanism of injury
Guillotine
Crush
Avulsion
Incidence
Friedrich et al J Hand Surg Am 2011
- 9400 upper extremity amputations
- 14.5% underwent replantation
- 27% thumbs, 12% digits, 12% hands or forearms
Indications for surgery
Thumb
Multiple digits
Individual digit distal to FDS insertion
Partial hand / through palm - replant far superior to prosthesis as lose sensation and power grasp
Almost any body part in child
Wrist or forearm
Above or below Elbow - only if sharply demarcated
Contra-Indications
Adult single digit proximal to FDS insertion
- poor results / stiffness
Ischaemic time distal to carpus
- > 12 hours warm ischaemia time
- > 24 hours cold ischaemia time
Ischaemic time proximal to carpus
- > 6 hours warm ischaemia time
- > 12 hours cold ischaemia time
Severe crush or mangled
Levels
- through elbow
- high arm
Multiple level / segmental injury
Other serious injuries / comorbidities
Transport of amputated part
4oC ideal
2 Methods
1. Wrapping the part in a moistened cloth of Ringer's or Saline
- placing in plastic bag and placing the bundle in ice water
2. Immersing the part in one of these solutions in a plastic bag
- then putting on ice
No difference in outcome
Most important is to give clear and precise instructions to referring doctors
Ischaemia
Key factor in success
Duration of allowed ischaemia varies from tissue to tissue
Recommended maximum
1. Distal to carpus
12 hours warm ischaemia time
24 hours cold ischaemia time
Digits consist of skin, bone and subcutaneous tissue
- no muscle
- warm ischaemia tolerated for long periods
- freezing not tolerated
- digits have survived for 12 hours or longer of warm ischaemia
- when cooled replants have been successfully performed at 36 hours
2. Proximal to carpus
6 hours warm ischaemia time
12 hours cold ischaemia time
Major limb replants contain large volume of muscle
- only tolerate 4-6 hours of ischaemia
- because of the size of the extremity only its outer part is adequately cooled
- the deep muscle remains relatively warm
- the allowable 6 hours warm ischaemia time can't be extended
Patient factors
High demand professionals
- may push indications
- i.e. amputation at level of proximal phalanx
Patient must be aware of chance at viability, function, time off work etc
Premorbid conditions must be taken into account
- diabetes, smoking, peripheral vascular disease
- patient compliance
Surgeon
Should be able to consistently achieve 90% patency rate in 1mm vessels in laboratory
Digits
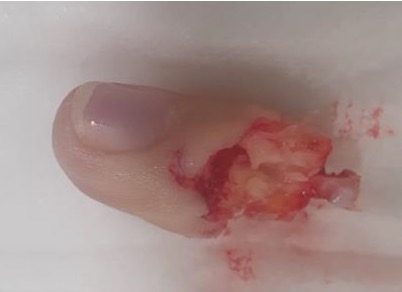
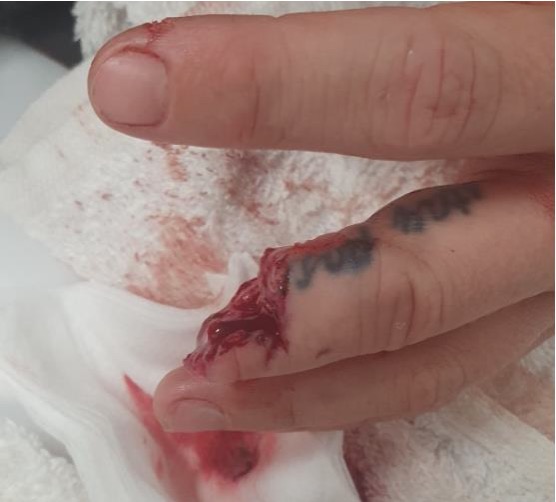
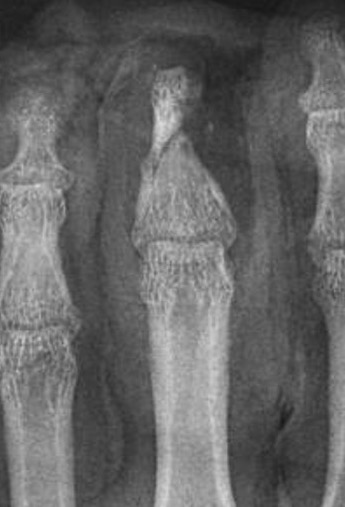
Single digit
Distal to FDS tendon insertion replant
- outcomes good
- able to immediately mobilise of digit
Proximal to FDS tendon insertion replant
- useful function does not occur
- patient will bypass finger
Multiple digits
Concept
- replant best digit to most useful stump
- when thumb intact goal is to restore palm width
Kaneshiro et al J Plast Reconst Aesthet Surg 2020
- retrospective review of 12 patients undergoing multiple digit replantation
- mean 2.8 digits replanted, survival 87%
Results
Survival
Shaterian et al J Hand Microsurg 2018
- systematic review of 32 studies with > 6000 digit replantations
- increased survival rates with 2 (90%) versus 1 (84%) arterial anastomoses
- increased survival rates with 2 (92%) versus 1 (73%) versus 0 (61%) venous anastomoses
- increased survival with sharp injuries (87%) versus crush (70%)
Function
- systematic review of 28 studies with 618 digit replants
- average grip strength 80% contralateral limb
- average two point discrimination 8 mm (normal 2 mm)
- average DASH score 12 (0 - no disability, 100 - severe)
Operative technique for single digit
Sequence
1. Locate and tag vessels and nerves
2. Debride
3. Shorten and fix the bone
4. Repair extensors
5. Repair flexors
6. Anastomose the arteries
7. Repair the nerves
8. Anastomose the veins
9. Obtain skin coverage
Technique
Set up
- maintain body temperature by warming the patient
- axillary block to block sympathetics
- ABx, tetanus prophylaxis
- in dwelling catheter
Approach
- longitudinal mid-lateral incisions for digital replants
Shorten bone
- get out of zone of injury
- must have no tension on the grafts
- minimum 0.5 - 1 cm each side
- alternative is to vein graft but is easier to shorten bone
- shortening also helps with skin coverage
- ORIF proximal phalanx
- K wire DIPJ / distal phalanx
Extensor Tendons
- primary repair
- if inadequate extensor tendon for primary repair perform delayed repair
Flexor tendons
- repaired primarily if at all possible
- otherwise 2 stage
Arterial repair
- 9/0 or 10/0 nylon interrupted
- key is repair normal intima to normal intima
- adventitia is intensely thrombogenic so ensure none in repair
- strip adventitia for 1-2mm
- repair both arteries if possible otherwise consider reversed vein graft
- tourniquet acceptable
- micro-clips / bulldog clips should not be applied > 30 min due to intimal damage
- heparin boluses to maintain patency (5000IU in 500 mls)
- papaverine antispasmodics
Vein repair
- 2 veins for every artery
- can consider removing nail bed + heparin soaked dressings to allow bleeding
Nerve repair
- 10/0 interrupted epineural repair
- primary repair if possible
- primary nerve graft or conduit
- use medial cutaneous nerve of forearm
Skin
- skin closed under no tension
- digital incisions often left open to decompress repairs
Postoperative management
Elevate in gallows
- high dependency area
- appropriate intravenous fluids
- anticoagulation controversial - usually heparin boluses given
- smoking strictly prohibited
- no caffeine
- warm ambient temperature
- observations hourly for 72h then q4h
Assessment of vascularity
Colour / capillary refill
Oxygen saturation probe
Surface temperature <30°C indicates that poor perfusion of the replant is certain
Pinprick
- bright red bleeding normal
- dark blue blood venous congestion
Failing replantation
If appears threatened immediate action is necessary
1. Relieve dressings or sutures
2. Either elevate or dependant position
3. Regional block for sympathetics
4. Relieve pain, fear and anxiety
5. Ensure patient warm and adequately hydrated
6. Intravenous heparin
7. Consider medical leeches for venous congestion
8. If return to OT is necessary then must be within 4-6 hours of ischaemia
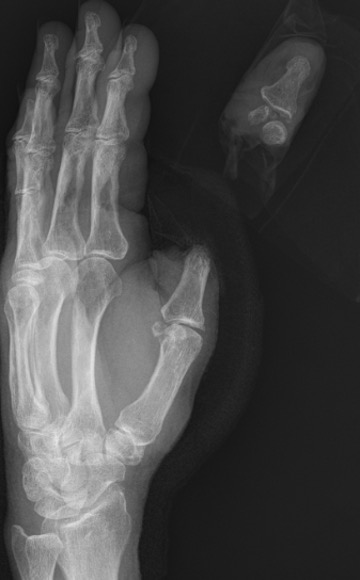
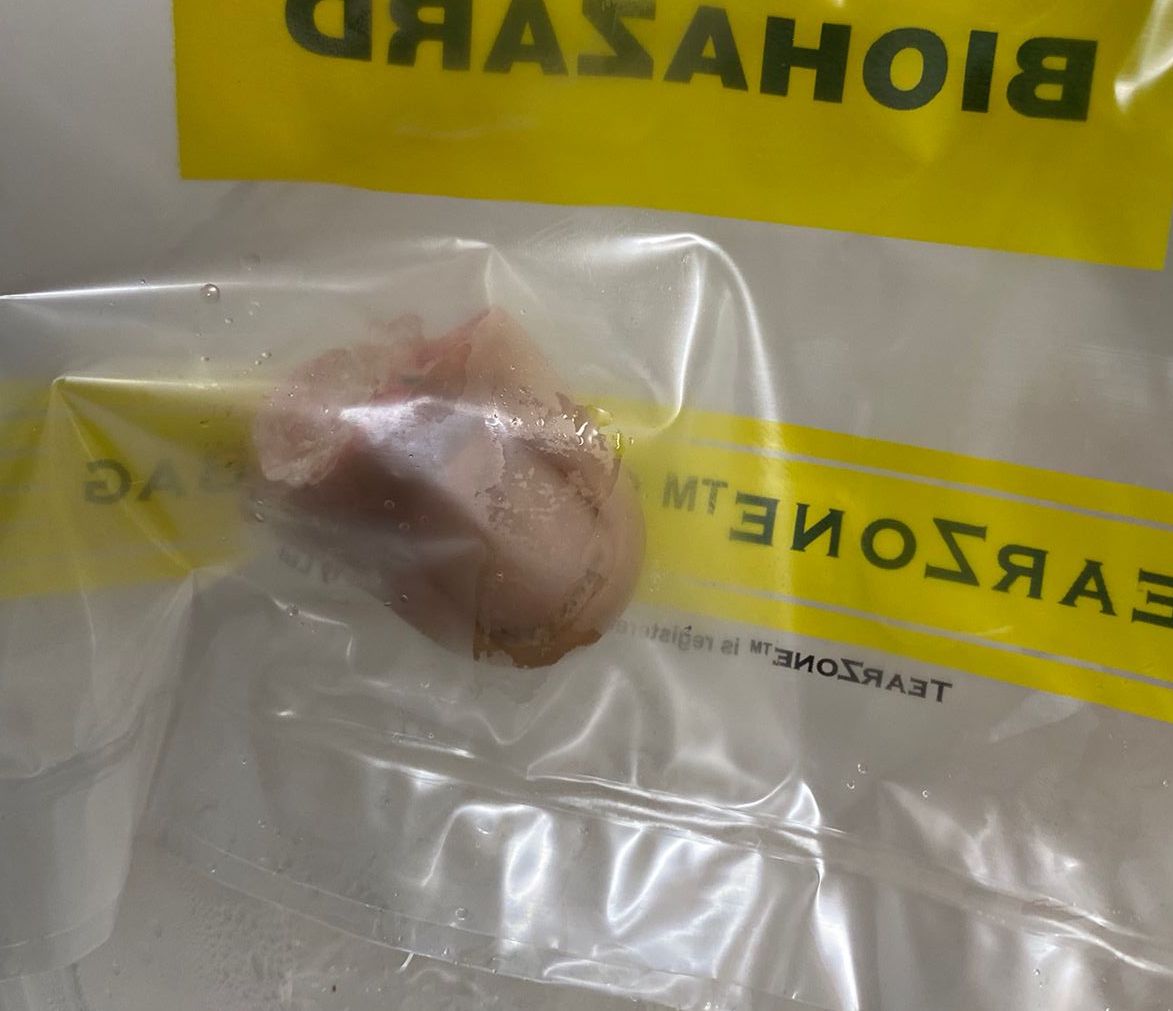
Thumb replant
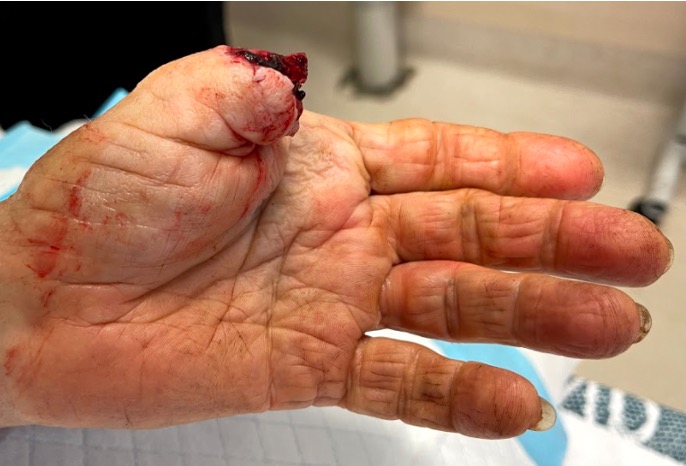
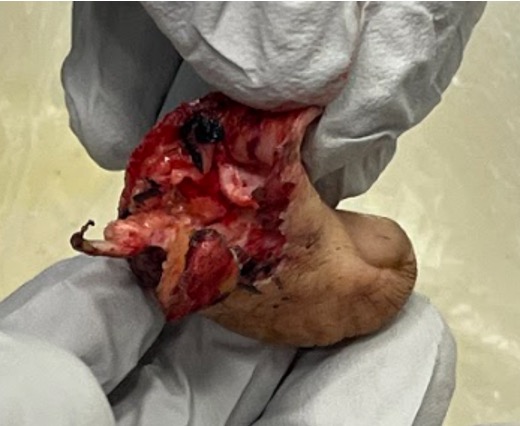
Background
Thumb has first priority
A successfully replanted thumb is always better than any reconstruction
- thumb provides 40% of hand function
- a fixed stump / post is very useful
Level
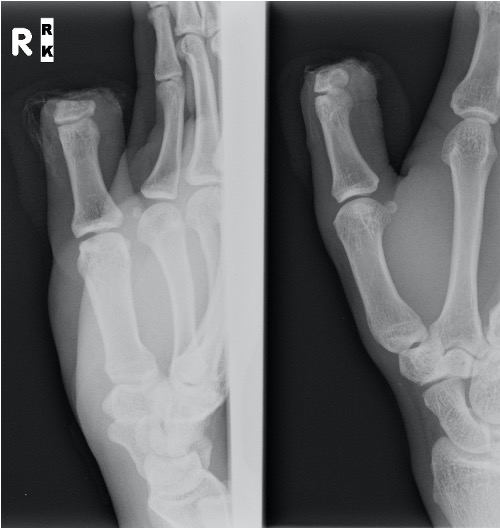
Detipped thumb can be successful
- need dorsal veins in stump
- need 4mm of skin proximal to nail plate
- all efforts should be made to preserve thumb length
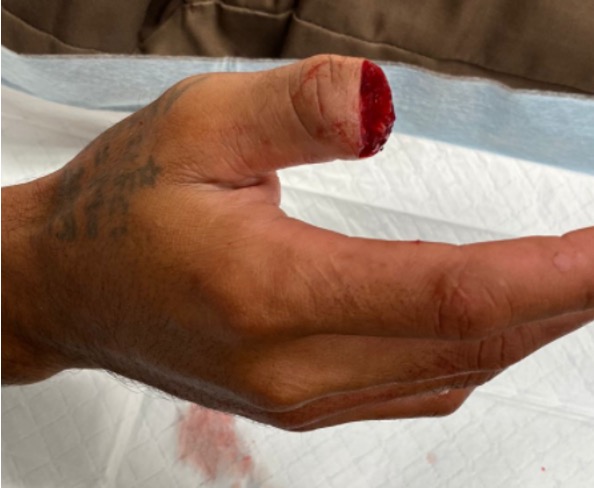
Technique
Ulnar sided artery larger
Need to adduct shoulder / internally rotate arm
Can fuse IPJ
Salvage
- systematic review of toe to thumb transfer for traumatic thumb replantation
- 25 studies, 450 cases
- 101 second toe transfers
- 196 great toe transfers
- similar outcomes
Ring Avulsions
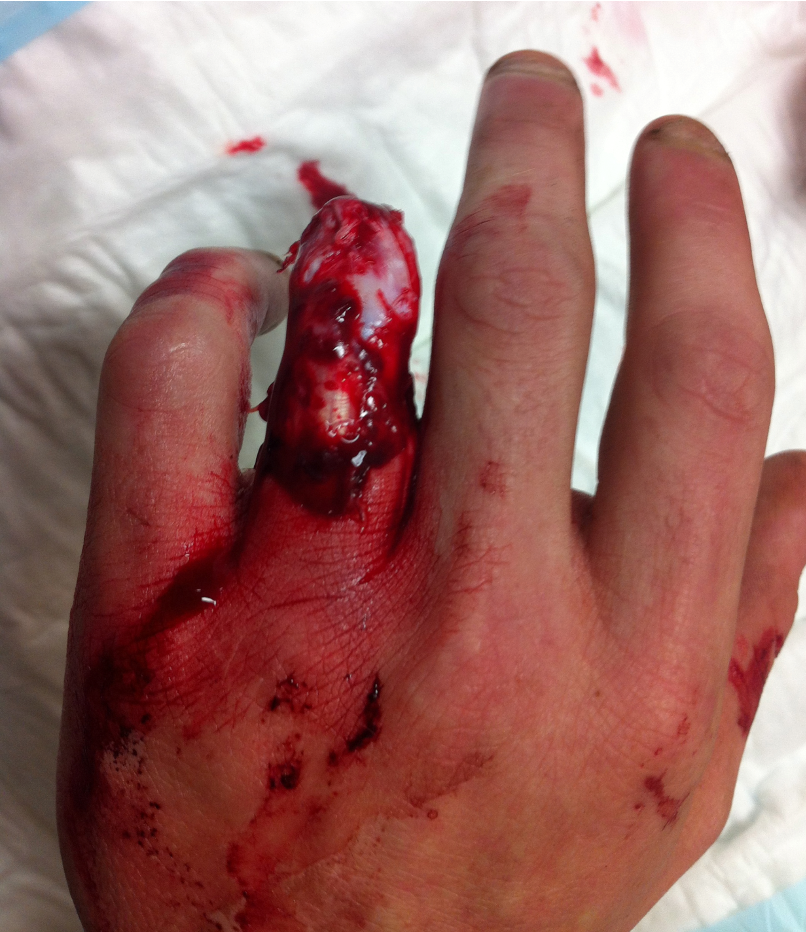
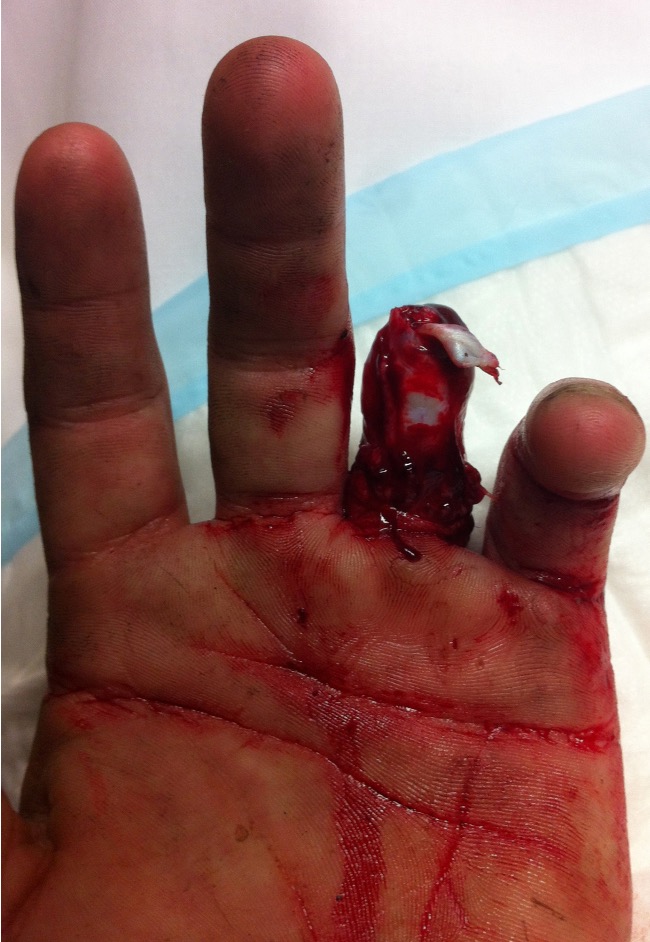
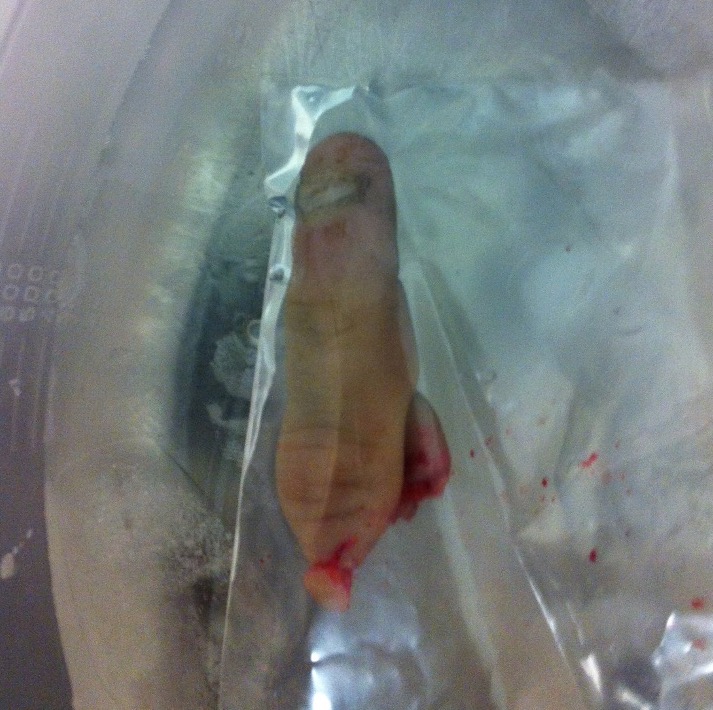
Definition
Circumferential skin loss of finger caused by traumatic injury to ring
Urbaniak Classification
- systematic review
Type I
- circulation adequate
- may involve damage to flexor / extensor tendons
- 9% of injuries
- typically good results
Type II
- circulation inadequate
- typically microvascular repair less simple
- can be large zone of injury
- vascular grafts or venous flaps may be required
Type III
- complete degloving or complete amputation
- 84% survival with replantation
- worse outcomes with regards range of motion and two-point discrimination
Midcarpal Replantation
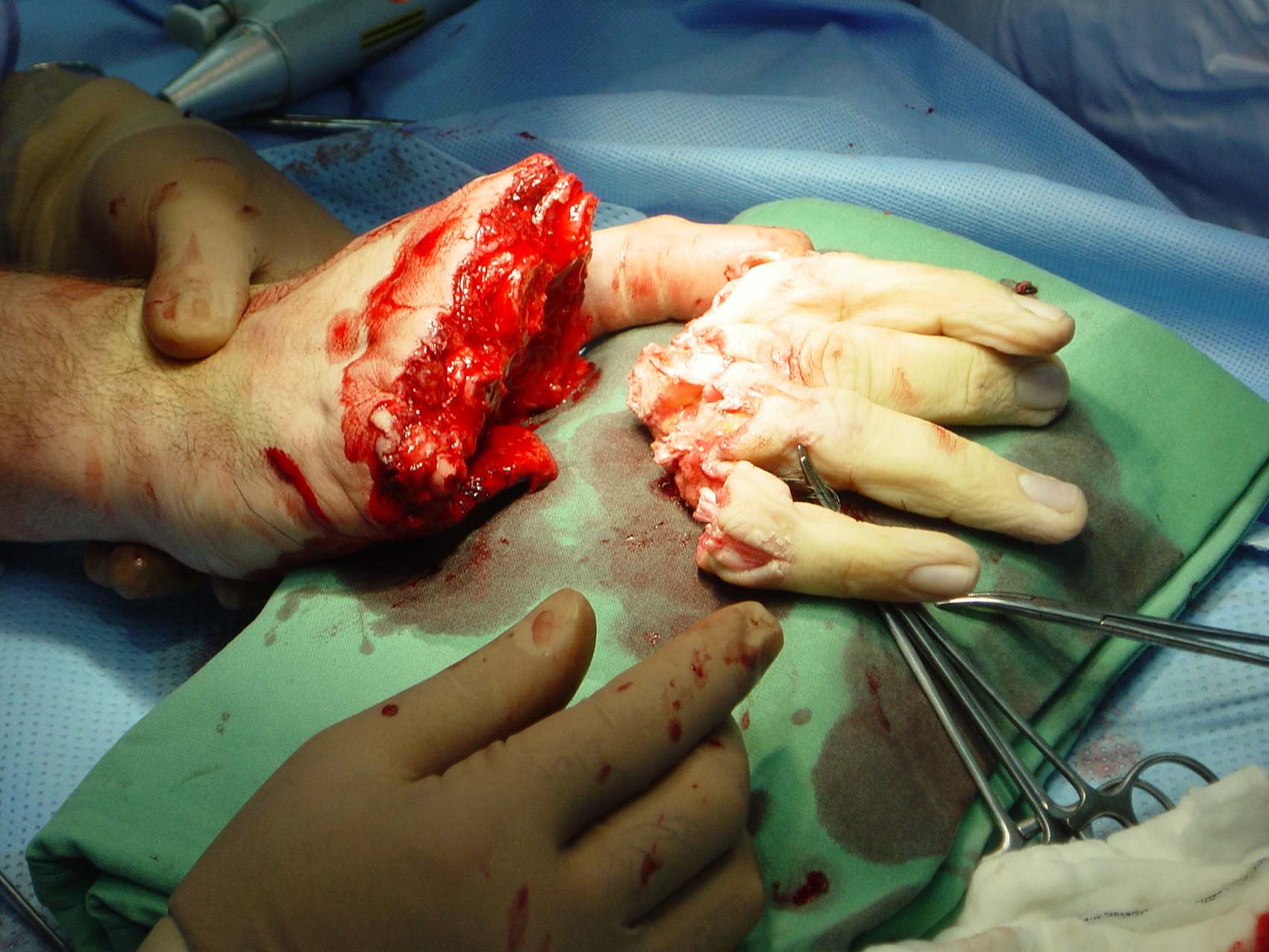
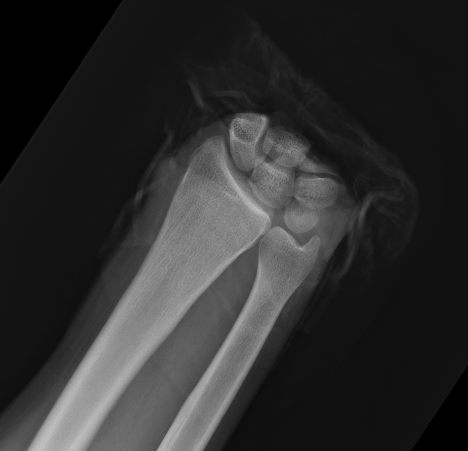
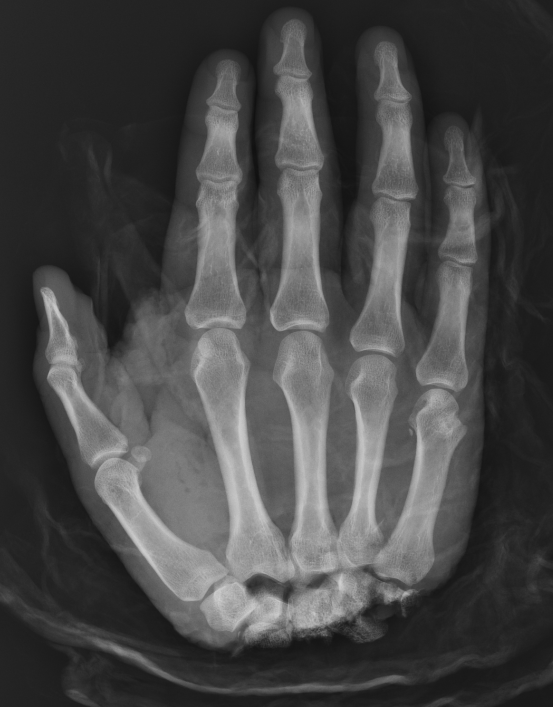
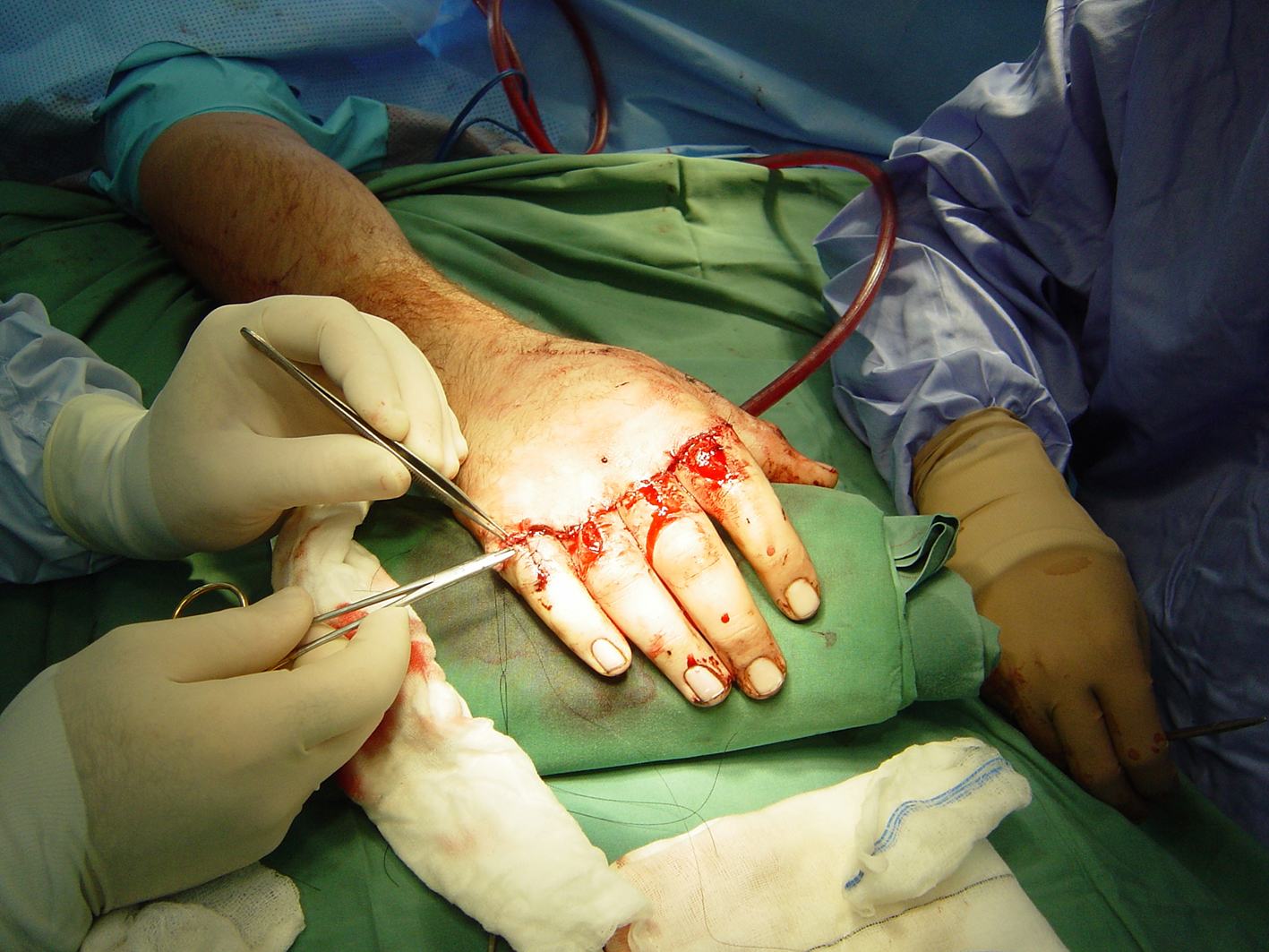
Major Limb Replantation
Definition
Proximal forearm / elbow joint / arm
Issues
1. Usually avulsion or crush injuries types with extensive muscle injury
2. Amputations proximal to metacarpal level have significant muscle bulk
- high risk of myonecrosis and subsequent infection
- immediate arterial inflow is necessary
- need patient hydration and osmotic diuresis to protect kidneys
3. Functional outcome related to level of amputation
Technique
Rapid skeletal stabilisation
- at least one artery must be revascularised
- then follow sequence for digit
- extensive fasciotomies always indicated
- any exposed vessels must be covered by rotation flap etc
Results
Ramji et al Plast Reconstr Surg Global Open 2020
- systematic review of 13 studies with 136 major limb replantation
- functional outcome related to level
- good to excellent outcome scores distal to elbow
- poor outcomes at or proximal to elbow
